Ctrl + F is the shortcut in your browser or operating system that allows you to find words or questions quickly.
Ctrl + Tab to move to the next tab to the right and Ctrl + Shift + Tab to move to the next tab to the left.
On a phone or tablet, tap the menu icon in the upper-right corner of the window; Select "Find in Page" to search a question.
Share UsSharing is Caring
It's the biggest motivation to help us to make the site better by sharing this to your friends or classmates.
Bacteria
Bacteria, which are microscopic organisms that play diverse roles, from aiding digestion to causing infections, are essential for Earth's ecosystems.
microorganisms
prokaryotes
pathogens
antibiotics
infections
reproduction
evolution
respiration
diversity
growth
metabolism
plasmids
resistance
mutation
biofilm
We eat fungi?
- True
- False
Tests performed in BRAIN HEART INFUSION BROTH
- Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
- Novobiocin Susceptibility Test
- Optochin Susceptibility Test
- Polymyxin B Susceptibility Test
- 20% Dextrose Strip Test
- Salt Tolerance Test
two substances found in viruses
- nucleic acid/DNA or RNA
- nucleic acid/DNA or RNA
- plasmid
- capsid
Image: https://media.quizizz.com/_mdserver/main/media/resource/gs/quizizz-media/quizzes/9ee94e9e-34b9-43d7-b93e-cecda6a17fd9-v2?w=90&h=90

- Image: https://media.quizizz.com/_mdserver/main/media/resource/gs/quizizz-media/quizzes/9ee94e9e-34b9-43d7-b93e-cecda6a17fd9-v2?w=90&h=90
- Select one:
- Question text
Which of the following is a viral infection?
- cholera
- influenza
- strep throat
- tuberculosis
35. What is the primary function of the bacterial cytoplasm?
- a) Contains enzymes and cellular structures
- b) Stores genetic material
- c) Synthesizes ATP
- d) Facilitates cell movement
91. What is the term for bacteria that obtain energy from sunlight?
- a) Phototrophs
- b) Chemotrophs
- c) Heterotrophs
- d) Autotrophs
44. Which of the following bacterial diseases is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
- a) Tuberculosis
- b) Tetanus
- c) Strep throat
- d) Salmonellosis
66. Which of the following bacterial diseases is transmitted through contaminated food and can lead to paralysis?
- a) Tuberculosis
- b) Botulism
- c) Cholera
- d) Tetanus
Which microorganisms are harmful? CHECK ALL THAT APPLY!
- salmonella
- salmonella
- e coli
a protein coat surrounding viral DNA
- capsid
- capsule
- endospores
- microbiota
What are types of bacteria?
- Tetanus (Missed)
- Tetanus (Missed)
- Authorax
- Salmonella (Missed)
- Streptococci (Missed)
- Pneumonia (Missed)
- Ecoil
- Staphlorocco (Missed)
5. Which bacterial structure allows for movement?
- a) Flagella
- b) Cilia
- c) Pili
- d) Capsule
29. Which bacterial species is commonly used in the fermentation of dairy products like yogurt?
- a) Salmonella
- b) Escherichia coli
- c) Lactobacillus
- d) Clostridium
Bacteria are....
- Unicellular
- Unicellular
- Multicellular
- Prokaryotic
- Microscopic
Which scientist created tests that helped confirm that bacteria and other microorganisms cause a variety of diseases?
- Robert Koch
What are examples of Viruses?
- Ecoil
- Tetanus
- Common Cold (Missed)
- Flu (Missed)
- HIV (Missed)
- Herpes (Missed)
- Chicken Pox (Missed)
Algae is the largest producer of ___________________ on Earth.
- pond scum
- bacteria
- oxygen
- carbon dioxide
86. Which bacterial structure is responsible for transferring genetic material from one bacterial cell to another during conjugation?
- a) Ribosome
- b) Conjugation pilus
- c) Flagellum
- d) Capsule
Microorganisms are so small they can only be seen ________________.
- From the sky
- In a science lab
- through a microscope
- in the dirt
The ________ is used by some bacteria to move around in their environment
- flagella
Tests performed in MUELLER-HINTON AGAR
- Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
- Novobiocin Susceptibility Test (Missed)
- Optochin Susceptibility Test
- Polymyxin B Susceptibility Test (Missed)
How many named species of bacterias are there?
- 40000
- 1500
- 30000
- 8000
Viruses and some bacteria can be classified as pathogens because they
- provide oxygen
- cause disease
- recycle nutrients
- can be used to produce medicine
Which statement is true about viruses?
- Viruses can eat and metabolize food.
- Viruses can reproduce only using a host cell.
- Viruses can reproduce on their own at any time.
- Viruses contain DNA, so they are alive.
58. Which of the following bacterial diseases can lead to severe lung infection and is caused by Legionella pneumophila?
- a) Tuberculosis
- b) Tetanus
- c) Cholera
- d) Legionnaires' disease
54. Which of the following bacterial diseases is transmitted through contaminated water and causes severe diarrhea?
- a) Tetanus
- b) Anthrax
- c) Cholera
- d) Plague
Bacteria have short, fine, hairlike appendages called ______
- plasmids
- flagella
- spirillia
- pilli
Can a virus change the normal activity of a cell?
- No
- Maybe
- Yes
What would happen to a bacterial cell if its protective covering was destroyed?
- It would be harmed by chemicals in the environment.
Which ones are ALPHA HEMOLYTIC
- S. pyogenes
- S. agalactiae
- S. dysgalactiae
- S. equi
- S. equisimilis
- S. zooepidermicus
- S. bovis (Missed)
- S. equinus (Missed)
- E. faecalis (Missed)
- E. avium (Missed)
- E. durans (Missed)
- E. faecium (Missed)
- S. pneumoniae (Missed)
- S. anginosus (Missed)
- S. mutans (Missed)
- S. mitis (Missed)
- S. salivarius (Missed)
- S. sanguis (Missed)
The kingdom containing disease-causing bacteria and most of the helpful bacteria is
- Eubacteria
- Archaebacteria
_Select the statements that support the fact that viruses are not alive.
- Viruses are unicellular.
- Viruses are not made of cells.
- Viruses need a host cell to survive.
- Viruses cannot reproduce on their own.
68. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing dental decay?
- a) Escherichia coli
- b) Clostridium
- c) Streptococcus pneumoniae
- d) Streptococcus mutans
90. Which of the following bacterial diseases is transmitted through contaminated water and causes severe diarrhea?
- a) Tetanus
- b) Anthrax
- c) Cholera
- d) Plague
Ribosomes are also found in bacteria cell.
- True
- False
What can bacteria do?
- - they can cause disease- they can help us digest our food
73. What is the primary function of bacterial endospores?
- a) Energy production
- b) Survival in harsh conditions
- c) Protein synthesis
- d) DNA replication
name the shape
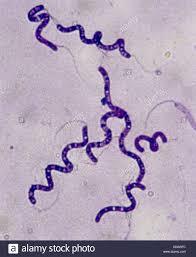
- spirillum (spiral shaped)
- bacillus (rod-shaped)
- coccus(sphere)
What is the whip-like 'tail' that bacteria use for movement?
- Cell wall
- Ribosome
- Flagella
- Cytoplasm
_Select each of the following structures that are found in a virus.
- genetic material
- genetic material
- nucleus
- cell membrane
- capsid (protein coat)
bacteria has
- no cell wall and no cell membrane
- both cell wall and cell membrane
- cell wall
- cell membrane
77. What is the primary function of bacterial capsules?
- a) Protection from immune cells
- b) Energy production
- c) Nutrient absorption
- d) DNA replication
32. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing food poisoning?
- a) Escherichia
- b) Streptococcus
- c) Salmonella
- d) Clostridium
17. Which of the following bacterial infections is typically transmitted through contaminated food or water?
- a) Influenza
- b) Salmonella
- c) Tuberculosis
- d) HIV
a cell infected by a virus
- capsid
- plasmid
- capsule
- host cell
Bacteria are classified as prokaryotes because they are missing
- a cell wall
- genetic material
- a nucleus
- ribosomes
Identify the energy sources used by autotrophic bacteria
- decaying matter
- sunlight
- inorganic chemicals
What is cytoplasm?
- Jel-like fluid that fills the cells and gives it shape
- Bone-like structure that give it protection
- Small structure that makes protein
- Whip-like structure that allows for movement
How does a virus reproduce?
- With a female virus
- By controlling a cell to make copies
- They cant reproduce
What is the cell part labeled as "E"
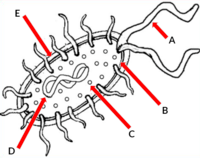
- Cell wall
What process is this?
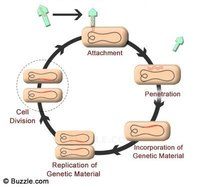
- phagocytosis
- lytic cycle
- lysogenic cycle
- formation of antibodies
The gene for antibiotic resistance is found in the ________ inside the bacterial cell. Not all bacterial cells have this structure.
- plasmid
57. What is the primary function of bacterial ribosomes?
- a) Storage of genetic material
- b) Protein synthesis
- c) Energy production
- d) Cell division
How long ago did the first life (bacteria) appear on Earth?
- 300 years ago
- 3,000 years ago
- 3 million years ago
- 3.5 billion years ago
22. Which of the following bacterial diseases has been largely eradicated through vaccination programs?
- a) Polio
- b) Tuberculosis
- c) Cholera
- d) Malaria
The two economic disadvantages of bacteria are food spoilage and
- parisitism
- production of antibiotics
- antibiotic resistance
- human disease
Which bacteria cell part goes in the box labelled a?

- Flagella
- Chromosomal DNA
- Ribosomes
- Plasma Membrane
Name a virus that you can be vaccinated for (BESIDES COVID)
- flu
harmful or helpful: bacteria helps ruminants digest cellulose
- helpful
- harmful
These organisms only have one cell.
- single-cell organisms
- multi-cell organisms
- plants
- humans
A bacterium reproduces asexually by dividing to form two new bacterial cells. What is the name of the process by which bacteria reproduce?
- meiosis
- mitosis
- budding
- binary fission
The segment of DNA injected into host cells by a virus is called the
- prophage
- capsid
- plasmid
- prion
Which of these is characteristic of both viruses and bacteria?
- They get their energy from their environment.
- They can reproduce on their own.
- They can form crystals and become dormant.
- They contain proteins and nucleic acids.
Bacteria reproduce in which way?
- Sexually (binary fission)
- Budding
- Meoisis
- Asexually (binary fission)
93. What is the primary function of bacterial capsules?
- a) Protection from immune cells
- b) Energy production
- c) Nutrient absorption
- d) DNA replication
100. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing botulism?
- a) Streptococcus
- b) Clostridium
- c) Escherichia coli
- d) Salmonella
- I hope these questions help with your study of bacteria!
69. What is the primary function of bacterial capsules?
- a) Protection from immune cells
- b) Energy production
- c) Nutrient absorption
- d) DNA replication
What type of virus is the Sars-CoV-2 (corona virus)?
- Retrovirus
- Oncovirus
- Bacteriophage
- Prion virus
15. Which of the following is an example of a nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
- a) Escherichia coli
- b) Rhizobium
- c) Streptococcus
- d) Staphylococcus
Bacteria are....(select all that apply)
- Single-celled organisms
- Single-celled organisms
- Multi-cellular organisms
- Eukaryotes
- Prokaryotes
56. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing pneumonia?
- a) Streptococcus
- b) Clostridium
- c) Streptococcus pneumoniae
- d) Escherichia coli
what does the cell membrane do
- helps to transport ions, nutrients, and waste.
harmful or helpful: bacteria keep less friendly cells from growing in or on your body
- helpful
- harmful
Which type of microorganism is the LARGEST?
- Bacteria
- Algae
- Fungus
- Virus
Name a BACTERIA that you can get a vaccine for:
- diphtheria
How do viruses move?
- By fluid blood (Missed)
- By fluid blood (Missed)
- By hand contact (Missed)
What does pili do?
- It allows dna to be transferred from one bacterium to another
Which viral structure is responsible for attaching the virus to the host cell?
- capsid
- tail sheath
- tail fiber
- genetic material
How would you get Bacillus Cereus?
- Improperly cooking food, at lower temperatures.
- Infection through infected animal or soil
- By eating smoked fish or improperly canned foods at home
- Innoculated with trama into muslcles
- Penetration of skin by a rusted nail
Identify the long whip like structure used for movement
- pili
- flagella
- capsule
- plasmid
Bacteria...
- include yeast
- are prokaryotic
- do not grow in UV light
- are eukaryotic
50. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing botulism?
- a) Streptococcus
- b) Clostridium
- c) Escherichia coli
- d) Salmonella
48. Which bacterial disease is characterized by the formation of a hard, protective case around the bacterial cell?
- a) Tuberculosis
- b) Anthrax
- c) Cholera
- d) Tetanus
Which applies to S. pneumoniae
- Bile esculin positive
- 6.5% NaCl positive
- Optochin sensitive (Missed)
- Bile soluble (Missed)
20. What is the primary function of bacterial endospores?
- a) Reproduction
- b) Survival in harsh conditions
- c) Protein synthesis
- d) Energy production
46. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing urinary tract infections?
- a) Escherichia
- b) Escherichia coli
- c) Streptococcus
- d) Salmonella
Which applies to Staphyloccocus spp.
- Fermentative (Missed)
- Fermentative (Missed)
- Oxidative
- Oxidase negative (Missed)
- Oxidase positive
- Bacitracin resistant (Missed)
In continuous flow culture,
- there is more product
- there are only two stages: lag and stationary
- it is more used by the industries
- you cannot do water treatments
What do prokaryotes have on the outside of their cell membrane that gives protection and support?
- the cell wall
bacteria have no what?
- nucleus
27. Which of the following bacterial structures is involved in the exchange of genetic material during conjugation?
- a) Capsule
- b) Nucleoid
- c) Pilus
- d) Endospore
Match the scientist with his contribution to our understanding of disease:
- discovered bacteria Leeuwenhoek
- developed vaccine for Polio Salk
- developed vaccine for Small Pox Jenner
- viruses contain DNA Hershey & Chase
how are Archaea different from Bacteria?
- they don't have peptidoglycan and bacteria has peptidoglycan
- they don't have peptidoglycan and bacteria has peptidoglycan
- they are similar to eukaryotic cells
- bacteria is similar to prokaryotic cells
82. Which of the following bacterial diseases is transmitted through contaminated water and causes severe diarrhea?
- a) Tetanus
- b) Anthrax
- c) Cholera
- d) Plague
Image: https://media.quizizz.com/_mdserver/main/media/resource/gs/quizizz-media/quizzes/38a884e5-71d6-41c2-a87c-507a25e09b60-v2?w=90&h=90

- Image: https://media.quizizz.com/_mdserver/main/media/resource/gs/quizizz-media/quizzes/38a884e5-71d6-41c2-a87c-507a25e09b60-v2?w=90&h=90
Endotoxins : 1) plasmid called pXO1 which has three different proteins a) edema factor (EF) b) ? c) ? and whats the second endotoxin? Finally, which bacillus is this?
- B) neurotoxin,c) lethal factor , Plasmid pX02, Bacillus anthracis
- b) Protective antigen(PA) c) Lethal Factor ( LF) and plasmid pX02 ; Bacillus anthracis
- B)tetanospasmin c) Protective antigen ; plasmid pXO2 ; Bacillus anthracis
- B) Protective antigen(PA) c) Lethal Factor ( LF) and plasmid pX02 ; Bacillus cereus
An heterotroph is a bacteria which gets its energy from
- autotrophs
- autotrophs
- eating
Multi-celled organisms are made up of ____________________ cells.
- one
- two
- multiple
- ten
52. Which bacterial structure is responsible for transferring genetic material from one bacterial cell to another?
- a) Capsule
- b) Conjugation pilus
- c) Flagellum
- d) Ribosome
Which of these is NOT a way that bacteria can be helpful?
- Aid in digestion of our food
- Protect against harmful bacteria
- Decompose organic matter in soil
- Fix nitrogen in soil for plants to use
- can become resistant to antibiotics
When do bacteria form endospores?
- In the best environment, i.e. enough food, enough
- When the temperature is ambient
- In harsh conditions
- When they are dormant
Which of the following is not a way that bacteria are able to move?
- Lashing or snaking forward
- Gliding through slime
- Flagella
- Pili
Which of the following are identified as archaeal groups?
- Methanogens
- Methanogens
- Eubacteria
- Halophiles
- Thermoacidophiles
Which structure is used by some bacteria for movement?
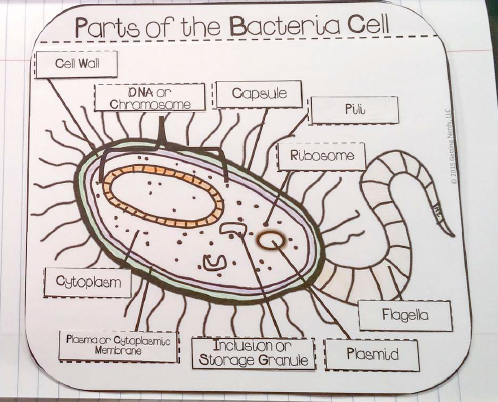
- flagella
What causes clostridium perfringens?
- Colonizes pharaynx
- Innoculated with trauma into muscles (Missed)
- Necroticskin exposed to bacteria, growing and damaging local tissue. (Missed)
95. What is the term for bacteria that thrive in extremely cold environments?
- a) Psychrophiles
- b) Thermophiles
- c) Acidophiles
- d) Halophiles
Where do bacteria store sugars and lipids?
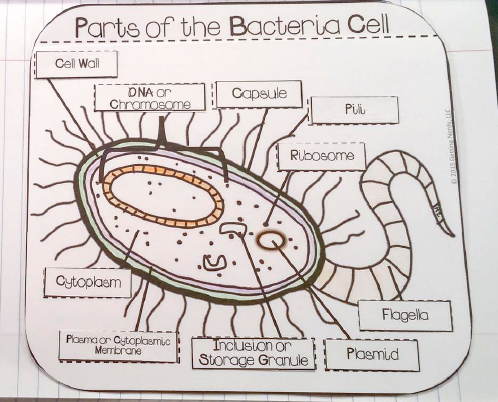
- storage granule
55. What is the term for bacteria that live in the absence of oxygen and are often found in the digestive tract?
- a) Aerobic
- b) Anaerobic
- c) Facultative anaerobic
- d) Microaerophilic
What type of virus uses RNA that is translated in hosts to create new viruses?
- oncoviruses
- retroviruses
- prophages
- viroids
87. What is the term for bacteria that thrive in extremely cold environments?
- a) Psychrophiles
- b) Thermophiles
- c) Acidophiles
- d) Halophiles
what are the surface structures of bacteria?
- capsule, cell wall, and cell membrane
Which form of bacteria is matched correctly to its description?
- coccus—can cause MRSA and has a round shape
where is nucleoid?
- it is in the middle and floating
a latent virus can remain in the body for years before destroying the host cells
- true
- false
Match the pandemic-causing pathogen to its method of spreading & causing illness: (from EdPuzzle)
- contaminated water; caused death by dehydration Cholera
- sexual contact or from mom to newborn during birth Syphilis
- respiratory or thru infected fabrics Small Pox
- infected fleas biting humans Plague / Black Death
- mosquito bites Yellow Fever
96. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing urinary tract infections?
- a) Escherichia
- b) Escherichia coli
- c) Streptococcus
- d) Salmonella
Which of the following is true?
- Viruses and bacteria are both prokaryotes.
- Bacteria are eukaryotes and viruses are prokaryotes.
- Some bacteria are prokaryotes and some are eukaryotes.
- All bacteria are prokaryotes.
The carbohydrate found in the cell walls of Eubacteria is called
- cellulose
- peptidoglycan
- glucose
- chitin
harmful or helpful: bacteria help make foods
- helpful
- harmful
16. What is the primary mode of nutrition for autotrophic bacteria?
- a) Heterotrophy
- b) Photosynthesis
- c) Predation
- d) Parasitism
88. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing urinary tract infections?
- a) Escherichia
- b) Escherichia coli
- c) Streptococcus
- d) Salmonella
Bacteria are _______, meaning they have _______ _____________________
- Prokaryotes; no nucleus
- Prokaryotes; no DNA
- Eukaryotes; no nucleus
- Eukaryotes; no DNA
Bacteria of decay are important components of an ecosystem because they
- are involved in photosynthesis
- recycle organic matter
- absorb solar energy
- slow the spread of disease
Pathogens cleans of oil spills
- True
- False
harmful or helpful: bacteria "fixes" nitrogen
- helpful
- harmful
do bacteria have a nuclei?
- no
- yes
Which ones are BETA HEMOLYTIC
- S. pyogenes (Missed)
- S. pyogenes (Missed)
- S. agalactiae (Missed)
- S. dysgalactiae (Missed)
- S. equi (Missed)
- S. equisimilis (Missed)
- S. zooepidermicus (Missed)
- S. bovis
- S. equinus
- E. faecalis (Missed)
- E. avium (Missed)
- E. durans (Missed)
- E. faecium (Missed)
- S. pneumoniae
- S. anginosus (Missed)
- S. mutans (Missed)
- S. mitis (Missed)
- S. salivarius (Missed)
- S. sanguis (Missed)
There are approximately 10 times as many human cells as bacteria cells in the human body.
- True
- False
name the shape
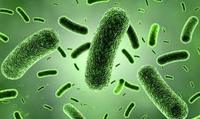
- spirillum (spiral shaped)
- bacillus (rod-shaped)
- coccus (sphere-shaped)
94. Which bacterial structure is responsible for transferring genetic material from one bacterial cell to another during conjugation?
- a) Ribosome
- b) Conjugation pilus
- c) Flagellum
- d) Capsule
the outside of a bacterial cell is protected by a structure called a
- capsule
21. Which type of bacteria stain purple in the Gram staining process?
- a) Gram-positive
- b) Gram-negative
- c) Gram-neutral
- d) Gram-variable
archaebacteria lives in extreme environments
- True
- False
53. What is the primary function of bacterial mesosomes?
- a) Energy production
- b) Protein synthesis
- c) DNA replication
- d) Cell division
ways you can limit the spread of viral infections
- covering your mouth when coughing
- covering your mouth when coughing
- healthy diet
- be vaccinated
7. Which of the following is a beneficial role of bacteria in the human body?
- a) Causing diseases
- b) Digesting food in the gut
- c) Filtering blood
- d) Producing antibodies
36. Which of the following bacterial structures is involved in DNA replication?
- a) Flagellum
- b) Capsule
- c) Pilus
- d) Nucleoid
49. What is the primary function of bacterial inclusions?
- a) Storage of nutrients and metabolic byproducts
- b) Protein synthesis
- c) Energy production
- d) DNA replication
Which mode of reproduction is matched correctly with its description?
- transduction—virus transfers genes from one bacteria to another
A ______________ bacteria gets food from other organisms. They can be saphrophytes or parasitic bacteria.
- heterotrophic
is there a nucleus in a bacterial cell?
- no
61. What is the term for the process by which bacteria take up DNA from their surroundings and incorporate it into their genome?
- a) Conjugation
- b) Transduction
- c) Transformation
- d) Replication
Consider this microscopic image of bacteria.mc003-1.jpgBased on its shape, what is most likely the form of this bacteria?
- bacillus
Which ones are GAMMA HEMOLYTIC
- S. pyogenes
- S. agalactiae
- S. dysgalactiae
- S. equi
- S. equisimilis
- S. zooepidermicus
- S. bovis (Missed)
- S. equinus (Missed)
- E. faecalis (Missed)
- E. avium (Missed)
- E. durans (Missed)
- E. faecium (Missed)
- S. pneumoniae
- S. anginosus (Missed)
- S. mutans (Missed)
- S. mitis (Missed)
- S. salivarius (Missed)
- S. sanguis (Missed)
If bacteria are in a temperature that is too high for them, their enzymes become_________
- denatured
40. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing dental cavities?
- a) Salmonella
- b) Clostridium
- c) Streptococcus
- d) Lactobacillus
Which of the following Latin roots correctly describes the shape of these bacteria?
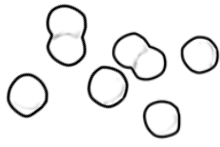
- bacillus
- coccus
- spirillum
- strepto
harmful or helpful: bacteria can give you strep throat
- helpful
- harmful
8. What is the primary function of the bacterial capsule?
- a) Oxygen exchange
- b) Protection from immune cells
- c) Nutrient absorption
- d) Reproduction
Check all of the non-living characteristics of viruses.
- They are non-cellular.
- They are non-cellular.
- They can mutate or change.
- They have no metabolism.
- They can crystallize.
What percentage of bacteria are harmful to humans?
- 10%
- less than 1%
- 90%
- more than 100%
binary fission
- the process of cell division in prokaryotic organisms by which the parent cell divided into two genetically identical cellsby asexual reproductionvery rapid reproductionSTeps; dna molecule is copieddna molecules attach to cell membranecell membrane elongates and pinches off leaving two identical cells
Which of the following creates genetic variation among bacteria?
- binary fission
- conjugation
What does bacteria do?
- Break down carbohydrates
- Break down carbohydrates
- Help protect the cells in your intestines from invading pathogens
- Help us absorb fatty acids
- Promote repair of damaged tissue
Bacteria can be both helpful and harmful.
- True
- False
Match these symptons to the Bacteria A) severe muscle spasms ( lockjaw) B) Severe dihhera, abdominal cramps, feverC) general malaise to menegitis to spontaneous abortionsD) pockets of gas formation under skin, degrades muscles, limp muscles that secrete black fluid. E) Flaccid muscle paralysis, double vision, general muscle weakness, respiratory paralysis.F) Colonizes Pharaynx, forms grayish pseudomembrane composed of fibrin, leukocytes, exotoxins damage heart and neural cells
- A) Clostridium tetani
- B) Clostridium Difficile
- C) Listeria
- D) Clostridium Perfringens
- E) Clostridum Botulism
- F)Corynebaterium Dipheria
Where are viruses found?
- Almost everywhere
- Everywhere
What type of bacteria will be killed in the presence of oxygen?
- Obligate aerobes
- Obligate anaerobes
- Facultative anaerobes
- Photoautotrophs
You are looking at a sample under the microscope to see if your patient has a bacterial infection. When you look in the microscope, you see something that looks like this. Is it a bacterium?

- Yes, this is a bacterium
- No, this is not a bacterium
67. What is the term for bacteria that require high salt concentrations to grow?
- a) Halophiles
- b) Acidophiles
- c) Thermophiles
- d) Mesophiles
81. What is the primary function of bacterial endospores?
- a) Energy production
- b) Survival in harsh conditions
- c) Protein synthesis
- d) DNA replication
Which bacteria structure is labelled with the star?

- Cell Wall
- Capsule
- Ribosome
- Flagella
In batch culture, the product is collected during the two stages:
- log and decline
- log and lag
- lag and decline
- lag and stationary
cold sores are caused by a(n) _______ virus.
- active
- flu
- host
- latent
Tests performed in BLOOD AGAR PLATE
- Bacitracin Susceptibility Test (Missed)
- Bacitracin Susceptibility Test (Missed)
- Novobiocin Susceptibility Test
- Optochin Susceptibility Test (Missed)
- Polymyxin B Susceptibility Test
- 20% Dextrose Strip Test (Missed)
The segment of DNA that is shared between bacteria during conjugation is called the
- bacteriophage
- prophage
- capsid
- plasmid
what do plasmids do?
- they eat the other structures
- they can cause death to certain cells
- they have DNA strands that are separate from the main structure
- they take the DNA out of the cell
Which applies to Group B strep
- Hippurate positive (Missed)
- Hippurate positive (Missed)
- CAMP positive (Missed)
Which of these conditions would allow extremophile Archaebacteria to survive? (select all that apply)
- high temperatures
- high temperatures
- high salinity
- acidic conditions
- methane-rich
how does bacteria move?more then one answer
- Move by rushing fluid (Missed)
- Move by rushing fluid (Missed)
- Move by flagellum (Missed)
Who first discovered bacteria
- Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
- Galileo Galilei
- Hooke
- Hubert Blaine Wolfeschlegelsteinhausenbergerdorff Sr.
Harmful mold and other fungi can...Check ALL that apply.
- Rot wood
- Rot wood
- cause diseases
transduction
- a method of genetic recombination in bacteria in which dna is transferred between cells by a virus
Test/s that requires 37 degrees Celsius incubation and requires CO2
- Oxidation/Fermentation (Hugh-Leifson) test
- Bacitracin susceptibility test
- Novobiocin susceptibility test
- Polymyxin B susceptibility test
- Optochin susceptibility test (Missed)
- Mannitol Salt Agar (Staphylococci identification)
- CAMP Test (Missed)
- 20% Dextrose Strip Test
- Salt Tolerance Test (Your Answer)
- Bile solubility test (Missed)
how does an active virus reproduce?
- the viral DNA forces a host cell's own machinery to make more viruses
- the viral DNA forces the host cell to go through binary fission
- the viral DNA is replicated and passed on every time the host cell goes through mitosis
- all of the above
Bacterias are microscopic
- true
- false
39. What is the primary function of bacterial flagella?
- a) Locomotion
- b) Photosynthesis
- c) Protein synthesis
- d) DNA replication
3. What is the function of the bacterial cell wall?
- a) DNA replication
- b) Protein synthesis
- c) Providing structural support
- d) Energy production
What is a prokaryote?
- a unicellular organism that lacks internal membrane bound structures, including a membrane bound nucleus
Name and describe the two enterotoxins of bacillus anthracis and the3 different proteins associated with one of them.
- 1) Plasmid called PXO1 with three proteins a) edema factor ( EF) that disrupts water homeostasis b) protective antigen ( PA) that promotes the entry of EF into the phagocytic cell c) Lethal factor ( LF) zinc metalloprotease that inactivates protein kinease. 2) Plasmid PX02 that encodes 3 genes required for synthesis of poly-glutamyl capsule.
Bacterial is eukaryotic organisms
- true
- false
26. What is the primary role of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle?
- a) Carbon fixation
- b) Oxygen production
- c) Nitrogen fixation
- d) Phosphorus cycling
Viruses must bind to specific proteins on the cell surface because of this, animal viruses can only infect _______ cells.
- animal
Poly-D-glutamicacid protein capsule that prevents phagocytosis.
- Bacillus Cereus
- Clostridium Botulium
- Bacillus Anthracis
- Clostridium Tetani
- Listeria monotogenes
Which of these characteristics of living organisms are NOT present in viruses?
- made of cells
- made of cells
- evolve
- Obtain materials for energy
- reproduce
- grow & develop
Where is bacteria found?
- Everywhere
- Almost everywhere
10. What is the term for the process by which bacteria exchange genetic material through direct contact?
- a) Binary fission
- b) Conjugation
- c) Transformation
- d) Transduction
6. What is the role of pili in bacteria?
- a) Sensing the environment
- b) Attachment to surfaces
- c) Photosynthesis
- d) Respiration
name the shape

- spirillum (spiral shaped)
- bacillus (rod-shaped)
- coccus (sphere-shaped)
There are five kingdoms of life. Bacteria belong in the kingdom called______
- Monera
How do single-cell organisms move? Check all that apply
- flagella
- cilia
- change shape
- all the above
13. Which of the following bacterial structures is responsible for storing genetic material?
- a) Nucleus
- b) Nucleoid
- c) Endoplasmic reticulum
- d) Golgi apparatus
75. What is the term for bacteria that obtain energy from sunlight?
- a) Phototrophs
- b) Chemotrophs
- c) Heterotrophs
- d) Autotrophs
How does a virus get energy?
- It produces energy
- From host cell
- They dont need it
viruses aren't made of cells
- true
- false
Bacteria normally replicate through (a) but can use (b) when stressors force them to adapt. Some bacteria form an (c) to go dormant when conditions are poor.
- abinary fission
- abinary fission
- bconjugation
- cendospore
14. What is the term for the protective structures formed by some bacteria in response to adverse environmental conditions?
- a) Capsules
- b) Pili
- c) Endospores
- d) Cilia
Which microorganism can cause diseases and infections in people?
- Bacteria
- All of the above
- Fungus
- Virus
bacteria sometimes struggle to survive. some bacteria escape this with
- outerspores
- endospores
- binary fission
- archaea
The use of what modern technology has cause the rise in resistant bacteria
- vaccines
- antibiotics
- fertilizers
- solar panels
Are prokaryotes more or less simple than eukaryotes?
- more
What are the 2 types of kingdoms
- Eubacteria and archae
One important way to control the spread of viruses in through
- the use of vaccines
- drinking a lot of tea
- the use of other types of bacteria
- the use of antibiotics
74. Which of the following bacterial diseases is transmitted through contaminated water and causes severe diarrhea?
- a) Tetanus
- b) Anthrax
- c) Cholera
- d) Plague
what are the appendages?
- pill and flagellum
47. What is the term for bacteria that require organic compounds for energy and carbon sources?
- a) Heterotrophs
- b) Autotrophs
- c) Phototrophs
- d) Chemotrophs
Type of virus that can be spread from insects:

- oncovirus
- arbovirus
- retrovirus
- all of these
31. Which of the following bacterial diseases can be prevented through vaccination with the BCG vaccine?
- a) Tuberculosis
- b) Tetanus
- c) Cholera
- d) Malaria
18. What is the term for bacteria that require oxygen to grow?
- a) Aerobic
- b) Anaerobic
- c) Facultative anaerobic
- d) Obligate anaerobic
Which applies to Group D strep
- Bile esculin positive
- 6.5% NaCl positive
- Optochin sensitive
- Hippurate positive
Ribosomes located within bacteria are used to produce
- viruses
- chromosomes
- more bacteria
- proteins
19. Which bacterial structure is responsible for attaching to host cells during infection?
- a) Adhesins
- b) Ribosomes
- c) Plasmids
- d) Nucleoids
Which of the following is true for both bacteria and viruses?
- both contain genetic material
- can be killed using antibiotics
- have a cell membrane
- have a protein coat
Which applies to Enterococcus
- Bile esculin positive (Missed)
- Bile esculin positive (Missed)
- 6.5% NaCl positive (Missed)
79. What is the term for bacteria that thrive in extremely cold environments?
- a) Psychrophiles
- b) Thermophiles
- c) Acidophiles
- d) Halophiles
Which two enterotoxins are made by bacillus cereus ?
- 1) Heat labile Toxin- that causes nausea, abdominal pain, diahera, lasts 12-24 hours
- 2) heat stable toxin - similar to S. Aureus food poisining , short incubuation, severe nausea, slight dihhera.
What is the job of the cell wall in bacteria?
- To provide protection
- To make protiens
- To hold organelles in place
- To hold water and nutrients
How could you get clostridium tetani?
- By eating smoked fish or improperly canned foods at home
- Infection through infected animal or soil
- Improperly cooking food, at lower temperatures.
- Penetration of skin by a rusted nail
- Innoculated with trama into muslcles
What is the name of a virus that has RNA instead of DNA?
- Prophage
- Retrovirus
- Prions
- Viroids
Viruses are similar to _____ because they need a host cell to replicate themselves.
- decomposers
- autotrophs
- heterotrophs
- parasites
Which bacteria cell part goes in the box labelled with the star?

- Flagella
- Chromosomal DNA
- Plasmid DNA
- Cell Wall
Not all bacteria has a flagella
- True
- False
What is the yellow
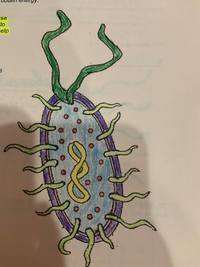
- DNA
- cell wall
- Cytoplasm
What do bacterias not have?
- Nucleus
41. What is the term for the protective mechanism that some bacteria use to resist the effects of antibiotics?
- a) Antibiotic resistance
- b) Biofilm formation
- c) Conjugation
- d) Transformation
11. Which of the following is a disease caused by bacteria?
- a) Tuberculosis
- b) Malaria
- c) AIDS
- d) Influenza
23. What is the term for the protective outer layer of some bacteria that helps them resist antibiotics?
- a) Biofilm
- b) Glycocalyx
- c) Mesosome
- d) Periplasm
Harmful bacteria can be found in raw meats, raw eggs, and other foods.
- True
- False
Which bacterial form can be curved like a spiral, thick and rigid, or thin and flexible?
- spirillum
What is the job of ribosomes in bacteria?
- To provide protection
- To make protiens
- To hold organelles in place
- To hold water and nutrients
conjugation
- the process by which a plasmid is transferred from one bacterial cell to another
80. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing urinary tract infections?
- a) Escherichia
- b) Escherichia coli
- c) Streptococcus
- d) Salmonella
do prokaryotes have a nucleus surrounding their chromosomes of dna?
- no
72. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing urinary tract infections?
- a) Escherichia
- b) Escherichia coli
- c) Streptococcus
- d) Salmonella
Bacteria can be found in
- The land only
- aquatic areas only
- temperate places on land
- every place ever
70. Which bacterial structure is responsible for transferring genetic material from one bacterial cell to another during conjugation?
- a) Ribosome
- b) Conjugation pilus
- c) Flagellum
- d) Capsule
60. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing diphtheria?
- a) Streptococcus
- b) Corynebacterium
- c) Clostridium
- d) Escherichia coli
Which is a reason that bacteria can cause infections in other organisms?
- Fast reproduction
We can produce products such as antibiotics or dairy products in a container known as a
- petri dish
- bioreactor
- test tube
- water bath
Which cell part is the thin, flexible covering of a cell that is semi-permeable?
- Cell membrane
- Cell wall
- DNA
- Cytoplasm
Protozoa serve valuable purposes. Which answers tell of this purpose. Check ALL that apply.
- Remove harmful waste from sewage at water treatment plants.
- Remove harmful waste from sewage at water treatment plants.
- Feed animals in the water.
12. What is the primary function of ribosomes in bacterial cells?
- a) Energy production
- b) Protein synthesis
- c) DNA replication
- d) Waste elimination
What do saprotrophs do (decomposers)
- Break down
- A process that uses bacteria to convert nitrogen into useful proteins
- Cleans up oil spills
Which viral life cycle kills its host cell by lysing (bursting)?
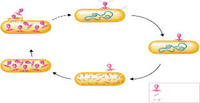
- Lysogenic Cycle
- Lytic Cycle
- Binary Fission
- Conjugation
We can live WITHOUT microorganisms.
- True
- False
- Sometimes
- During the spring and fall.
You can eat WITHOUT microorganisms.
- Yes
- No
- Sometimes
- Probably
Which of the bacterial structures protects the cell from drying out during times of stress?
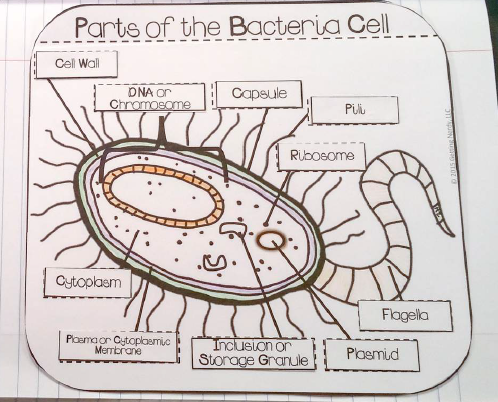
- capsule
99. What is the term for bacteria that obtain energy from sunlight?
- a) Phototrophs
- b) Chemotrophs
- c) Heterotrophs
- d) Autotrophs
When bacteria are stressed, what could happen? (select all that apply!)
- Conjugation - exchange of DNA between 2 bacteria
- Conjugation - exchange of DNA between 2 bacteria
- Mutation of DNA that leads to evolution / resistant bacteria
- Bacteria could die
Which of the following types of bacteria live on dead organic matter?
- Parasites
- Saprophytes
- Photoautotrophs
- Chemoautotrophs
What do viruses need to reproduce?
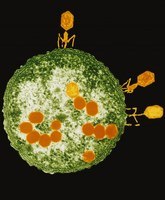
- they need genetic material
- They need a host cell
- They need bacteria
- They need insulin
24. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing strep throat?
- a) Escherichia
- b) Streptococcus
- c) Staphylococcus
- d) Salmonella
71. What is the term for bacteria that thrive in extremely cold environments?
- a) Psychrophiles
- b) Thermophiles
- c) Acidophiles
- d) Halophiles
There are 5 stages in the growth of bacteria: ___, log, stationary, decline and survival
- lag
Where can bacteria be found?
- Soil
- Soil
- Rock
- Ocean
- Arctic snow
Which applies to Micrococcus spp.
- Fermentative
- Oxidative (Missed)
- Oxidase negative
- Oxidase positive (Missed)
- Bacitracin resistant
- Bacitracin susceptible (Missed)
25. Which of the following bacterial diseases can be transmitted through the bite of an infected tick?
- a) Cholera
- b) Lyme disease
- c) Tuberculosis
- d) Malaria
small, circular strands of DNA
- plasmids
Describe 2-3 ways each that both viruses and bacteria can be helpful to humans.
- [No Answer]
What is in dark green
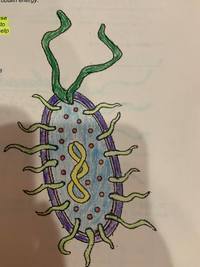
- cell membranes
- Flagella
- DNA
Why is the cytoplasm in cells important?
- It controls the activities of the cell
- It provides support and shape for the cell
- It controls what enters and exits the cell
- It keeps other cell parts from colliding and damaging each other
When a virus infects a host, it first attaches to the host cell, injects its genetic material, then
- assembles new viruses
- reads the genetic code
- releases new viruses
- destroys the host cell
Bacteria that stain red or pink are called
- gram positive
- gram negative
Which bacteria cell part goes in the box labelled with the star?

- Flagella
- DNA
- Plasma Membrane
- Cell Wall
what are the internal structures of bacteria?
- nucleoid, dna, and ribosomes
97. What is the primary function of bacterial endospores?
- a) Energy production
- b) Survival in harsh conditions
- c) Protein synthesis
- d) DNA replication
28. What is the term for bacteria that live in extreme environments, such as hydrothermal vents?
- a) Thermophiles
- b) Mesophiles
- c) Psychrophiles
- d) Halophiles
What are the symptons of Clostridium Difficile?
- Pockets of gas formation under skin, degrades muscles, limp muscles that secrete black fluid.
- Flaccid muscle paralysis, double vision, general muscle weakness, respiratory paralysis.
- Severe muscle spasms ( lockjaw)
- Severe dihhera, abdominal cramps, fever
- General malaise to menegitis to spontaneous abortions
63. What is the primary function of bacterial plasmids?
- a) Energy production
- b) Protein synthesis
- c) Genetic exchange
- d) DNA replication
Consider this microscopic image of bacteria. mc005-1.jpgWhich bacterial shape is shown in the image?
- spiral
43. What is the term for bacteria that obtain energy from sunlight?
- a) Phototrophs
- b) Chemotrophs
- c) Heterotrophs
- d) Autotrophs
harmful or helpful: bacteria are decomposers
- helpful
- harmful
98. Which of the following bacterial diseases is transmitted through contaminated water and causes severe diarrhea?
- a) Tetanus
- b) Anthrax
- c) Cholera
- d) Plague
Test/s that requires 35 degrees Celsius incubation
- Oxidation/Fermentation (Hugh-Leifson) test
- Oxidation/Fermentation (Hugh-Leifson) test
- Bacitracin susceptibility test
- Novobiocin susceptibility test
- Polymyxin B susceptibility test
- Optochin susceptibility test
- Mannitol Salt Agar (Staphylococci identification)
- CAMP Test
- 20% Dextrose Strip Test
- Bile solubility test
- Salt Tolerance Test
- Hippurate hydrolysis test (Missed)
Which bacteria cell part goes in the box labelled b?

- Flagella
- Chromosomal DNA
- Ribosomes
- Cell Wall
the bacterial DNA and ribosomes enclosed in a tough case that can survive unfavorable conditions
- host cell
- microbiota
- endospore
- plasmid
78. Which bacterial structure is responsible for transferring genetic material from one bacterial cell to another during conjugation?
- a) Ribosome
- b) Conjugation pilus
- c) Flagellum
- d) Capsule
What do doctors use to prime our immune systems to resist viruses?
- antibiotics
- vaccines
- gene therapy
- chemotherapy
Bacteria that are considered "extremophiles" because of the harsh environments they inhabit are in the kingdom

- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria
- both kingdoms
Bacteria can have the following shapes:
- cocci, bacilli, spirilla
- cocci, helical, rods
- complex, helical, polyhedral
- complex, cocci, spirilla, helical
Which microorganism is the SMALLEST?
- bacteria
- algae
- fungus
- virus
BONUS QUESTION (+2 points):Which microorganism is one of the oldest things on Earth?
- algae
Which part of the bacteria is always present?
- Cell wall
- Plasmid
- Flagella
- Capsule
a vaccine gives your body _______.
- the antibiotics needed to fight a virus
- a weakened or dead form of the virus
- a latent form of the virus
- peptidoglycan to resist a virus attack
Which is the 3 correct parts of bacteria?
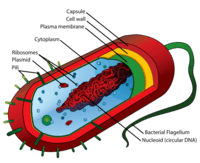
- Cell wall, DNA, Pili
- DNA, Plasmid, Nucleus
- Vacuole, Cell wall, Pili
- Plasmids, Cell membrane, Oytoplasm
What is the most outside part of a bacterium?
- Ribosome
- Cytoplasm
- Cell membrane
- Cell wall
What are the two bacteria kingdoms?
- -archaebacteria- eubacteria
What is the name of the disease-causing particle that does not contain DNA or RNA?
- Prophage
- Retrovirus
- Viroids
- Prions
What is the cell part labeled as "B"
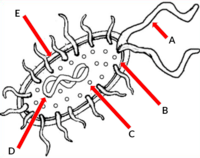
- Cell membrane
37. What is the term for bacteria that obtain energy from inorganic substances?
- a) Chemotrophs
- b) Phototrophs
- c) Heterotrophs
- d) Autotrophs
89. What is the primary function of bacterial endospores?
- a) Energy production
- b) Survival in harsh conditions
- c) Protein synthesis
- d) DNA replication
spirillum
- bacteria with an elongated spiral shapeexample: cholera
Which reason best explains why bacteria can reproduce quickly?
- Binary fission
Prokaryotes will often move by a tail-like what?
- flagellum
how can you prevent viral infections?
- by washing your hands regularly
- by eating a balanced diet
- by being vaccinated
- all of the above
2. What is the shape of a spherical bacteria cell?
- a) Spiral
- b) Cuboidal
- c) Round
- d) Rod-shaped
64. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing bubonic plague?
- a) Yersinia
- b) Clostridium
- c) Escherichia coli
- d) Salmonella
Some bacteria are autotrophs. This means they
- eat each other
- make their own food
- become parasites
- use chemicals to break down their food source
How was the Quizziz :^)
- [No Answer]
What are the three common shapes of bacteria's
- Spirilli round and rod shaped
- Sprilli bacilli and cocci
- Round spirals and Rod shape
Bacteria reproduce asexually by _ and sexually by _.
- binary fission, conjugation
Which series lists the correct order of steps of binary fission from first to last?
- DNA is copied ® DNA molecules attach to cell membrane ® cell membrane elongates and pinches off ® two identical cells are produced
What process occurs when bacteria break down nitrogen gas into a form that plants can use?
- binary fission
- conjugation
- nitrogen fixation
- decomposition
Identify the statements that correctly describe Archaebacteria.
- Archaebacteria were discovered in the 1970s.
- Archaebacteria were discovered in the 1970s.
- Archaebacteria live in almost all habitats on Earth.
- Archaebacteria have tRNA similar to eukaryotes.
- Archaebacteria do not have peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
92. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing botulism?
- a) Streptococcus
- b) Clostridium
- c) Escherichia coli
- d) Salmonella
how does bacteria reproduce?
- binary fission
- fussion
- meiosis
- mitosis
33. What is the term for the process by which bacteria break down
- a) Photosynthesis
- b) Decomposition
- c) Nitrogen fixation
- d) Fermentation
What do all viruses have?
- Protein Coat (capsid)
- Protein Coat (capsid)
- DNA or RNA (Missed)
the slimy coating around a bacterium
- plasmid
- capsule
- capsid
- host cell
45. What is the primary function of bacterial plasmids?
- a) Locomotion
- b) Genetic exchange
- c) Energy production
- d) Protein synthesis
Bacteria and fungi are __________________________.
- Producers
- Consumers
- Decomposers
- Mushrooms
For LC, we learn about three types of bacteria: round, ___ and spiral
- rod
The hair like structure in bacteria cell are called
- Nucleus
- Flagella
- Mitochondria
- Cell wall
transformation
- a type of gene transfer in which dna is taken from the environment
A obligate anaerobe is a type of bacteria that
- must have oxygen in its system
- cannot have oxygen in its system
- may or may not need oxygen
- uses sulfur dioxide
the helpful microscopic bacterial cells that inhabit your body
- host cell
- microbiota
- endospores
- plasmid
Match the bacteria shapes to the name:
- Bacilli
Organisms WITHOUT a nucleus?
- Bacteria
- Fungus
- Amoebas
- Virus
What are the 3 ways bacteria get energy ( food)
- Autotroph consumer mushroom
- Photosynthesis heterotroph autotroph
- Autotroph heterotroph saprotroph
Which of the following fungi are HELPFUL? Check ALL that apply.
- e coli
- yeast
- salmonella
- penicillin
4. Which of the following is a method of bacterial reproduction?
- a) Binary fission
- b) Mitosis
- c) Meiosis
- d) Budding
1. Which of the following is not a domain of life?
- a) Eukarya
- b) Bacteria
- c) Archaea
- d) Protista
Bacteria are found in which of the following places?
- in your digestive system
- in the air
- in soil
- all of the above
coccus
- bacteria with a spherical shapeexample: staph infection
how does bacteria get transmitted?
- Hands (Missed)
- Hands (Missed)
- Insects (Missed)
- Cold weather
- Microwaved food unproperly (Missed)
bacillus
- bacteria with a rod shapeexample: E. coli
What is bacteria?
- single-celled organisms that have no nucleus and can either benefit or harm the body
Bacteriophage is a virus that can infect bacteria.
- True
- False
65. What is the term for the process by which bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use?
- a) Photosynthesis
- b) Nitrogen fixation
- c) Fermentation
- d) Respiration
Which of the following bacteria use energy from inorganic reactions as a source of energy to build glucose?
- Parasites
- Saprophytes
- Photoautotrophs
- Chemoautotrophs
34. Which of the following bacterial infections can lead to the formation of pus-filled abscesses?
- a) Tuberculosis
- b) Lyme disease
- c) Cholera
- d) Staphylococcal infection
What is the cell part labeled as "C"
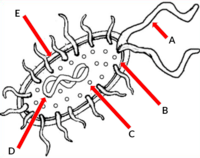
- Ribosome
Which of the following characteristics promote bacterial growth?
- Suitable temperature 30-50 degrees F
- Moisture
- Darkness
- Space to grow
An autotroph is a bacteria which gets its energy from ________
- photosythesis
- photosythesis
- sun
Image: https://media.quizizz.com/_mdserver/main/media/resource/gs/quizizz-media/quizzes/5a9148af-e6ca-49fa-96ba-c6218945c6fa-v2?w=90&h=90

- Question text
42. Which of the following bacterial infections is transmitted through the bite of infected fleas?
- a) Tuberculosis
- b) Plague
- c) Cholera
- d) Tetanus
thorough hand washing is able to prevent bacterial infections but isn't successful at preventing viral infections.
- true
- false
How does bacteria get energy
- They dont need it
- Binary fission (Missed)
- Conjuction (Missed)
30. What is the primary function of the bacterial cell membrane?
- a) Regulating the passage of substances in and out of the cell
- b) Synthesizing proteins
- c) Storing genetic material
- d) Providing structural support
What are the symptons of Clostridium Botulium?
- Flaccid muscle paralysis, double vision, general muscle weakness, respiratory paralysis.
- Pockets of gas formation under skin, degrades muscles, limp muscles that secrete black fluid.
- General malaise to menegitis to spontaneous abortions
- Severe dihhera, abdominal cramps, fever
- Severe muscle spasms ( lockjaw)
76. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing botulism?
- a) Streptococcus
- b) Clostridium
- c) Escherichia coli
- d) Salmonella
83. What is the term for bacteria that obtain energy from sunlight?
- a) Phototrophs
- b) Chemotrophs
- c) Heterotrophs
- d) Autotrophs
What part of bacteria sell helps it stick to surfaces
- Flagella
- RNA
- pilus
Which Gram Positive- spore- making Bacillius produces neurotoxins that blocks acetylcholine from the nerve terminals in ANS?
- Clostridium Botulium
- Clostridium tetani
- Bacillus Anthracis
- Listeria monotogenes
- Bacillus Cereus
9. Which type of bacteria can survive extreme conditions, such as high temperatures and acidity?
- a) Extremophiles
- b) Gram-negative bacteria
- c) Pathogenic bacteria
- d) Aerobic bacteria
What does semi-permeable mean?
- Keeps everything out
- Let's certain things in
- Let's everything in
plasmid
- a small, circular dna molecule in bacteria
84. Which bacterial genus includes species responsible for causing botulism?
- a) Streptococcus
- b) Clostridium
- c) Escherichia coli
- d) Salmonella
This structure is formed when bacteria are placed into unfavorable growth conditions....
- endospore
- crystallization
- pili
- plasmid
Test/s that requires 37 degrees Celsius incubation and does not require CO2
- Oxidation/Fermentation (Hugh-Leifson) test
- Bacitracin susceptibility test (Missed)
- Novobiocin susceptibility test (Missed)
- Polymyxin B susceptibility test (Missed)
- Optochin susceptibility test
- Mannitol Salt Agar (Staphylococci identification)
- CAMP Test
- 20% Dextrose Strip Test (Missed)
- Bile solubility test
- Salt Tolerance Test (Missed)
There are two types of food processing we have to learn: _____ and continuous flow culture
- batch
a virus has a, ______, a protein coat that surrounds its nucleic acid.
- capsid
- capsule
- cell membrane
- cytosol
59. What is the term for bacteria that require a low pH (acidic environment) to thrive?
- a) Acidophiles
- b) Alkaliphiles
- c) Halophiles
- d) Mesophiles
Name some bacterias
- Lactobacillus bulgaricus
- Lactobacillus bulgaricus
- Amoeba
- Pneumococcus
85. What is the primary function of bacterial capsules?
- a) Protection from immune cells
- b) Energy production
- c) Nutrient absorption
- d) DNA replication
51. What is the term for bacteria that can grow in the presence or absence of oxygen?
- a) Aerobic
- b) Anaerobic
- c) Facultative anaerobic
- d) Obligate anaerobic
62. Which bacterial structure is responsible for protecting the cell from its external environment?
- a) Cell membrane
- b) Nucleoid
- c) Ribosome
- d) Flagellum
Bacteria that require oxygen in order to survive are called
- Obligate anaerobes
- Obligate aerobes
- Facultative anaerobes
38. Which of the following bacterial diseases is caused by a spirochete bacterium?
- a) Tuberculosis
- b) Strep throat
- c) Salmonellosis
- d) Syphilis
Which kingdom of bacteria is more closely related to eukaryotes?
- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria
what does the cell wall do?
- it provides a rigid structure that gives the cell its shape
Which microorganisms help your body digest food?
- bacteria
- algae
- fungus
- virus
To keep up this site, we need your assistance. A little gift will help us alot.
Donate- The more you give the more you receive.
Related SubjectWalking Pneumonia: Causes and Trends
Cell Theory
Gender and Society
Prehistoric Sloths in Brazil
Tadpoles: From Water to Land
Life Science
Biology
Anthropology
Vibrant Triangle Indian Community
Kamala Harris: Insights into the Vice President’s Life and Work
Learning Communities
Understanding Culture Society and Politics
The Teacher and the Community School Culture and Organizational Leadership
Special Topics in Human Resource Management
Teaching Social Studies in Elementary Grades: Culture and Geography
Multi Cultural Diversity in Workplace for the Tour
Introduction to Criminology
Social and Professional Issues
Big Lots Business Insights
Introduction to inflation
Retail Sales Surge in October
Investment Strategies: Palantir Generational Stock
United States Markets Surge
Entrepreneurship Information
Barber Shop Business Plans
Small Business Management
Venture Capital
Strategic Business Analysis
Strategy Management and Acquisition
Adipose Tissue
Calculus-Based Physics 2
Show All Subject
Affiliate Links
Shopee Cashback Voucher
Temu $0 Shipping Fee
Amazon 75% Off Discounts