Ctrl + F is the shortcut in your browser or operating system that allows you to find words or questions quickly.
Ctrl + Tab to move to the next tab to the right and Ctrl + Shift + Tab to move to the next tab to the left.
On a phone or tablet, tap the menu icon in the upper-right corner of the window; Select "Find in Page" to search a question.
Share UsSharing is Caring
It's the biggest motivation to help us to make the site better by sharing this to your friends or classmates.
Paramedic
A highly skilled medical professional to provide emergency medical care, including assessment, treatment, and transportation of patients in critical conditions.
emergency
medical
paramedic
ambulance
first aid
resuscitation
trauma
cpr
emt
triage
patient
healthcare
emergency response
stabilization
assessment
Automaticity is most accurately defined as the ability of the heart to
- Generate an electrical impulse from the same site every time
- Spontaneously conduct an electrical impulse between cardiac cells
- Generate its own electrical impulses without stimulation from nerves
- Increas or decrease its heart rate based on the body's metabolic need
The space between the second and third ribs is called the
- Third intercostal space
- Intrathoracic margin
- Second intercostal space
- Second subcostal margin
The drug name that is derived from its chemical composition is referred to as its:
- Official name
- Chemical name
- Generic name
- Trade name
The most effective method for decreasing morbidity and mortality associate dwith spinal cord injury is
- Rapid transportation to a trauma center
- Public education and prevention strategies
- Minimizing scene time to 10 minutes or less
- Routine use of spinal motion restriction precautions
A young woman attempted to commit suicide by cutting her wrist. Bright red blood is spurting from the injury site. After applying direct pressure, you should
- Apply supplemental oxygen and keep her warm
- Elevate her extremity above the level of the heart
- Apply direct pressure dressing and start a large bore IV
- Locate and apply digital pressure to the brachial artery
While establishing IO access in a critically ill patient, you locate the appropriate anatomic landmark, cleanse the site, and insert the IO catheter at a 45 degree angle. After attaching the IV line and turning the flow on, you note edema developing on the opposite side of the extremity. What has most likely happened
- Extravasation due to an inappropriate angle of IO catheter insertion
- Inadvertent entry of a large vein, causing infiltration
- Fracture of the bone with leakage of bone marrow into the soft tissue
- Acute osteomyelitis 2nd to inappropriate cleansing of the site
Which of the following chemicals corrode the skin and cause massive protein denaturing
- Chlorine
- Ammonium
- Sulfur mustard
- Hydrogen peroxide
A 33 year old man was burned when the hot water heater he was working on exploded. The patient has superficial and partial thickness burns to his face, neck and arms. your initial assessment reveals that he is restless and tachypneic. His BP is 80/54 and his heart rate is 120 beats/min and weak. you should
- Conclude that he is experiencing burn shock, start two large bore IV lines of normal saline, and administer fluids based on the parkland formula
- Assist his ventilations with a BVM, cover him with a blanket, and start a large bore IV of normal saline set at TKO
- Apply oxygen via nonrebreathing mask, cover his burns with cold moist dressings, start and IV with normal saline and give up to 4 mg of morphine for pain
- Administer high flow oxygen, keep him warm, start at least one large bore IV of normal saline, and administer fluid boluses to maintain adequate perfusion
Any motor or sensory deficits noted during the neurologic examination of a patient with a possible spinal cord injury
- Indicate a complete spinal cord injury
- Require you to repeat the initial assessment
- Should be documented and monitored
- Must be reported to the hospital at once
What airway technique do you use when you have a 50-yr-old male patient who was involved in a MVA, unresponsive, and snoring respirations?
- Head tilt chin lift
- Oral Airway
- Nasal Airway
- Jaw Thrust manuever
As air accumulates in the pleural space, the first thing to occur is
- Decreased pulmonary function
- Contralateral tracheal deviation
- Compression of the great vessels
- Marked decrease in venous return
A 90-year-old is at home, conscious, alert, and well oriented. His family thinks he should be seen at the hospital for a liver problem. The man refuses to be transported. Who has the right to make the patient go to the hospital?
- A judge
- The EMS crew
- The patient's doctor
- The patient's family
General care for an eye injury involves
- Applying direct pressure to the globe
- Irrigating the eye with sterile saline solution
- Covering both eyes to minimize further injury
- Applying a cold compress to the eyeball
You use this without delay for High-degree blocks. Such as Type II second degree, or third degree heart blocks.
- Atropine
- Lidocaine
- Sodium Bicarb
- Transcutaneous Pacing
When considering analgesia for a burn patient who is in severe pain, you must remember that
- Due to the risk of causing hemodynamic compromise,analgesia should be avoided in the field
- One half of the usual dose of narcotic analgesics should be given in order to avoid drug toxicity
- Benzodiazepines are preferred over narcotics because they are less likely to cause hypotension
- Burns increase the metabolic rate, which may necessitate higher than normal doses of analgesia
Intraabdominal bleeding may produce few signs and symptoms of trauma because
- The intraabdominal cavity can accommodate large amounts of blood
- Blood in the peritoneum can compress the aorta and maintain perfusion
- It takes approximately 4 liters of blood loss before signs of shock manifest
- The abdominal muscular can sustain massive blunt force without bruising
no image
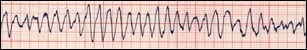
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Asystole
- 3rd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Inferior MI
- 1st Degree Heart Block
- Failure To Capture
- 2nd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Anterior MI
- Torsades
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Paced Rhythm
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
You are caring for a 41 year old man who was trapped in his burning house before being rescued by fire fighters. He has full thickness burns to his head and anterior trunk, and mixed partial and full thickness burns to both anterior upper extremities. What percent of his total body surface area has been burned
- 18%
- 27%
- 36%
- 45%
What drug may you give in place of Epinephrine?
- Lidocaine
- Sodium Bicarb
- Vasopressin
- Oxygen
The physician orders 5 mcg/kg/min of dopamine for an 80 kg patient. You put 400mg of Dopamine in 250 ml D5W. What is the correct rate using microdrip tubing?
- 15 gtts/min
- 120 gtts/min
- 30 gtts/min
- 40 gtts/min
Specific treatment for a hydrofluoric acid burn is
- Calcium chloride
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Magnesium sulfate
- Viscous lidocaine gel
What type of skull fracture is most common following high energy direct trauma to a small surface area of the head with a blunt object
- Depressed fracture
- Open fracture
- Basilar fracture
- Nondisplaced fracture
If you are having problems with Volume in a patient, what do you do?
- Give Fluids, Lasix, Morphine, Nitro, Check BP
- Give fluids, blood transfusions (if available), Consider Vasopressors, Cause specific interventions
- ABC's
- Call for Helicopter, Check ABC's, Give Fluids, Check BP, Furosemide, transport
You are ready to assist in initiating the induced hypothermia on a post cardiac arrest patient. Which intervention(s) will get the patient to the target temperature the fastest:
- Arctic Sun + Ice Packs
- Chilled Saline Only
- Chilled Saline + Arctic Sun
- Arctic Sun Only
A compression or burst fracture of the cervical spine would most likely occur following
- A direct blow to the occipital region of the skull
- Rapid acceleration following a motor vehicle crash
- Axial loading after a patient falls and lands feet first
- A significant fall in which the patient lands head first
When performing the standing takedown technique to immobilize a patient's spine, the patient is secured to the long backboard with straps
- While still standing position
- After the board is placed on the stretcher
- After a cervical collar has been applied
- After he or she is lowered to the ground
The following are all potential hazards to endotracheal intubation EXCEPT:
- Damage to the teeth
- Regurgitation
- Intubation of the right mainstem bronchus
- heart damage from rapidly increased oxygen
The primary risk associated with oral and dental injuries is
- Malocclusion
- Intraoral infection
- Permanent tooth loss
- Airway compromise
When assisting a patient to the bathroom, who is a fall risk, I should always use a "Bathroom Buggy"
- True
- False
The most significant sign of abdominal injury is:
- Tenderness
- Rigidity and guarding
- Pain
- Hematuria
Why do you want to give Oxygen to a patient with ACS?
- May limit ischemic myocardial injury, reducing the amount of ST segment elevation.
- Inhibits Thromoxane A2 platelet aggregation to reduce coronary reocclusion and recurrent events after fibrinolytic therapy.
- Dilates coronary arteries and vascular smooth muscle in veins, arteries, and arterioles.
- Dilates arteries and veins, which redistributes blood volume and reduces ventricluar preload and afterload.
Drugs that have alpha or beta sympathetic properties are called
- Vagolytics
- Sympathomimetics
- Parasympatholytics
- Adrenergic blockers
Which of the following is an aspect of professionalism?
- Being well groomed
- Maintaining patient confidentiality
- Attending continuing education sessions
- All of the above
Crucial to the efficient operations of EMS _____ are responsible for sending ambulances to the scene and ensuring system resources are in constant readiness
- Emergency Medical Radio Technicians
- Emergency Telecommunications Operators
- Emergency Medical Dispatchers
- Paramedical Telecommunications
Which document published in 1966 outlined the deficiencies in prehospital emergency care?
- National Standard Curriculum
- Accidental Death and Disability: The Neglected Disease of Modern Society
- EMS Agenda For The Future
- Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act
Patients with evidence of trauma above the _______ should be considered at risk for an associated spine injury
- Diaphragm
- Pelvis
- Umbilicus
- Clavicles
While hiking, a 24 year old woman was pinned from the waist down under a rock that collapsed on her. Upon your arrival, tha patient is conscious and alert, and states that she can't feel her legs. She further tells you that she thinks she's been pinned for about 5 hours. She is breathing adequately and has stable vital signs. In addition to administering supplemental oxygen, you should
- Start 2 large bore IVs of normal saline, apply a cardiac monitor, and contact medical control before removing the rock from her legs
- Quickly remove the rock from her legs to restore distal neurovascular function, and administer a 20 mL/kg blous of lactated ringers solution
- Administer 2 meq/kg of sodium bicarbonate followed by 25 gm of 50% dextrose as you slowly and carefully remove the rock from her legs
- Start at least one large bore IV line and administer 2-4 liters of normal saline before attempting to remove the rock from her legs
Cerebrospinal fuild is manufactured in the _______ of the brain and serves to_______
- Subdural space, prevent infection
- Cortex, protect the brain injury
- Ventricles, cushion and protect the bain
- Subarachnoid space, oxygenate the brain
After starting an IV in an arm vein for a patient with chest pain, and properly securing the catheter in place, you not that the IV is not flowing. You should
- Gently manipulate the catheter and reassess the flow
- Discontinue the IV and reestablish it in the other arm
- Ensure that the constricting band has been removed
- Use a pressure infuser device to improve the IV flow
no image
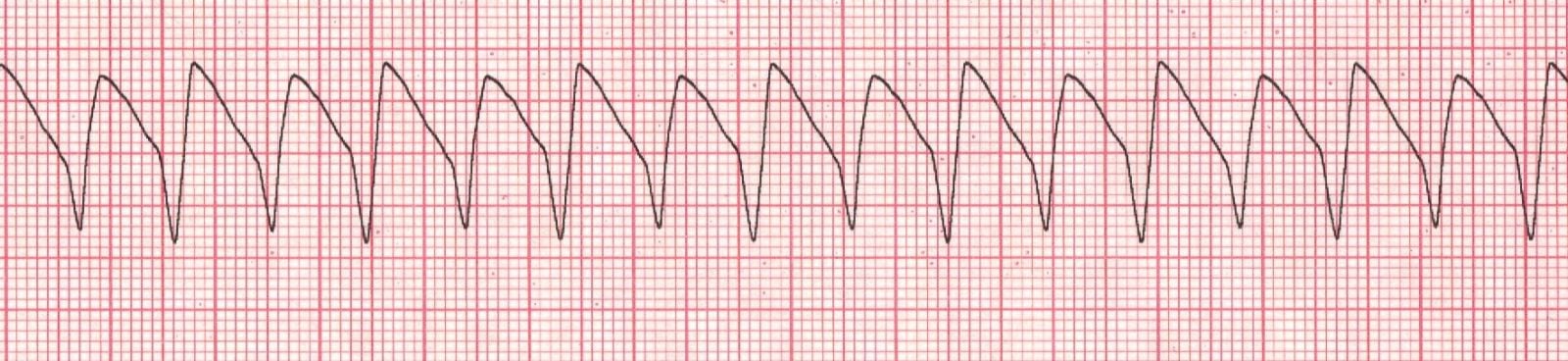
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Asystole
- 3rd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Inferior MI
- 1st Degree Heart Block
- Failure To Capture
- 2nd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Anterior MI
- Torsades
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Paced Rhythm
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
What medication is contraindicated in a Right-Sided Myocardial Infarction?
- Aspirin
- Plavix
- Beta-Blockers
- Nitroglcerin
A partial thickness burn is considered to be critical if it
- Occurs in any patient over the age of 45 years
- Is located to the proximal aspect of an extrmity
- Is rated as at least a 5 on a pain scale of 0-10
- Involves more than 30% of the body surface area
Which of the following drugs possesses beta-2 specific properties
- Dopamine
- Levophed
- Albuterol
- Epinephrine
Assessment of a patient who many have been exposed to radiation begins by
- Determining if the scene is safe to enter
- Thoroughly decontaminating the patient
- Quickly moving the patient to a safe area
- Evaluating airway, breathing, and circulation
Upper airway damge following a burn is most often caused by
- The inhalation of superheated gases
- Exposure to carbon monoxide or cyanide
- The inhalation of hot particulate steam
- Direct flame exposure to the oropharynx
What is the action of insulin?
- Transfers glucose into cells
- Stimulates alpha receptors
- Produces hemolysis of RBCs
- Produces glucagon
A young woman attempted to commit suicide by cutting her wrist. Bright red blood is spurting from the injury site. After applying direct pressure you should
- Apply supplemental oxygen and keep her warm
- Elevate her extremity above the level of her heart
- Apply a pressure dressing and start a large bore IV
- Locate and apply digital pressure to the brachial artery
When moving an injured patient from the ground onto a long backboard, it is generally preferred that you
- Slide the patient onto the backboard
- Use the four person log roll technique
- Log roll the patient away from you
- Apply the KED first
If the mechanism of injury indicated that your patient may have sustained a spinal cord injury
- Contact medical control to determine if spinal immobilization is needed
- Assume that a spine injury exists, regardless of the neurologic findings
- Apply a cervical collar and transport the patient in a position of comfort
- Fully immobilize the spine only if gross neurological deficits are present
Pramedics may function only under the direction and license of the EMS system's
- Town council
- Company owner
- Medical director
- Board of Directors
You are dispatched to a senior citizens center where an elderly woman apparently fainted. When you arrive, you find the patient sitting in a chair. An employee of the center tells you that he caught the patient before she fell to the ground. Your initial assessment reveals that the patient is conscious and alert and is breathing adequately. You should
- Forego spinal immobilization and transport only
- Obtain vital signs and assess her blood glucose level
- Apply oxygen at 15 liters per min via nonrebreathing mask
- Perform a rapid trauma assessment to detect injuries
After an adult victim is struck by lighting and experiences cardiac arrest
- Five minutes of CPR generally restores a pulse
- Perform a compression to ventilate ratio of 15:2
- His or her heart may resume beating spontaneously
- The ECG usually shows an organized cardiac rythm
Victims standing near an object that is struck by lightning
- Most commonly experience blast type injuries
- Often have areas of burns that resemble a fine red rash
- Typically experience intractable ventricular fibrillation
- Experience full thickness burns that require debridement
Dopamine has what effects when administered at 1-2 mcg/kg/min?
- Increased blood pressure
- Decreased blood pressure
- Renal and mesenteric dilation
- Decreased urine output
Nontraditional careers for paramedics include:
- Working in the primary care setting
- Providing emergency care on off-shore rigs
- Taking on occupational-safety role in an industrial setting
- All of the above
The atrioventricular junction
- Includes the AV node but not the bundle of His
- Is the dominant and fastest pacemaker of the heart
- Reveives its blood supply from the circumflex artery
- Is composed of the AV node and the bundle of His
The most acute complication associated with large body surface area burns is
- Infection
- Hypovolemia
- Hypothermia
- Myoglobinemia
Lidocaine is usually given for:
- Asystole
- Supreaventricular tachycardia
- Atrial fibrillation
- Ventricular tachycardia
The emerging roles and responsibilities of the paramedic include
- Public education
- Health promotion
- Participation in injury and illness prevention programs
- All of the above
The term that which describes normal respirations is:
- Orthopnea
- Eupena
- Bradypnea
- Dyspnea
There are two types of education in EMS: ______ and ____ education
- Prehospital, hospital
- Initial, continuing
- Clinical, field
- Initial, hospital
Common clinical findings associated with a subdural hematoma including all of the following, except
- Rapidly increasing ICP
- An underlying skull fracture
- A fluctuating level of consciousness
- Unilateral hemiparesis or slurred speech
While standing by at the scene of a structual fire, it is most important to remember that
- Toxic gases are often present, even after the fire is out
- The lead paramedic determines where you should stage
- Most fabric materials release cyanide when they burn
- You may need to provide rehabilitation for fire fighters
The problem with communciation of the elderly is most often due to:
- A hearing loss
- Confusion
- Senility
- Organic brain syndrome
What is the name for alveolar collapse?
- Pulmonary edema
- Tension pneumothroax
- Pneumonia
- Atelectasis
Image: https://www.proprofs.com/api/ckeditor_images/A-Flutter-Generated.jpg
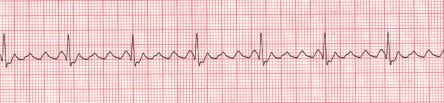
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Asystole
- 3rd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Inferior MI
- 1st Degree Heart Block
- Failure To Capture
- 2nd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Anterior MI
- Torsades
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Paced Rhythm
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
When immobilizing a sitting patient with a vest type extrication device, you should manually stabilize his or her head and then
- Apply an appropriately size cervical collar
- Perform a rapid assessment to detect life threats
- Assess distal pulse and sensory and motor function
- Carefully place the vest device behind the patient
Which of the following statements regarding the sinoatrial node is most correct
- The SA node is the dominant cardiac pacemaker in healthy patients
- The SA node is a backup cardiac pacemaker in healthy patients
- The SA node is located in the superior aspect of the right ventricle
- Impulses generated by the SA node travel through the right atrium only
Kinematics of trauma; How many collisions occur?
- One
- Two
- Three
- Four
Chronic subdural hematomas are most commonly seen in the patients who
- Are less than 2 years of age
- Have alcoholism
- Are prone to hypoglycemia
- Have high cholesterol
A 63 year old diabetic woman presents with an open wound to her forearm that she experienced when she fell a week ago. She tells you that the wound has been draining purulent fluid, but has not been bleeding. The wound itself is red, inflamed, and warm to the touch. You should
- Carefully irrigate the wound with sterile water for 5 minutes
- Apply a moist, sterile dressing and transport to the hospital
- Apply a dry, sterile dressing and transport her to the hospital
- Apply a light coat of antibiotic ointment and cover the wound
You are dispatched to a residence for a man who cut his hand with a chainsaw. Upon arriving at the scene your first action should be to
- Immediately gain access to the patient
- Apply gloves, a gown, and facial protection
- Determine if air medical transport is available
- Carefully assess the scene for safety hazards
If you are unable to orotracheally intubate a patient due to massive maxillofacial trauma and sever oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal bleeding, you would most likely have to perform
- Nasotracheal intubation
- A needle or surgical cricothyrotomy
- Pharmacologically assisted intubation
- Digital intubation
You are the first unit to arrive at the scene of a small building collapse. As you exit the ambulance, you can see a man pinned under a large metal beam. You should
- Free patient first and then assess him
- Carefully access the patient and assess him
- Contact medical control for further guidance
- Immediately request a special rescue team
The most significant complication associated with prolonged immobilization of a patient on a long backboard is
- Pressure lesion development
- Compression of the vena cava
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Patient discomfort and frustration
Changes in cardiac contractility may be induced by medications that have a positive or negative__________effect
- Vasoactive
- Dromotropic
- Inotropic
- Chronotropic
Which of the following statements regarding the thorax is most correct
- The thoracic cavity extends to the ninth or tenth rib posteriorly
- The diaphragm inserts into the anterior thoracic cage below the fifth rib
- The dimensions of the thorax are defined inferiorly by the thoracic inlet
- The dimensions of the thorax are defined anteriorly by the thoracic vertebrae
A young man was assaulted and has extensive maxillofacial injuries. Your initial assessment reveals that he is semiconscious, has poor respiratory effort, and has blood draining from the corner of his mouth. Initial management for this patient involves
- Inserting an oropharyngeal airway, preoxygenating him with a BVM for 2 minutes, and then intubating his trachea
- Applying a cervical collar, performing a blind finger sweep to clear his airway, and providing ventilatory assistance with a BVM
- Fully immobilizing his spine, inserting a nasopharyngeal airway, and hyperventilating him wit a BVM device at a rate of 20 beaths/min
- Manually stabilizing his head in a neutral position, suctioning his oropharynx, and assisting ventilations with a BVM device and 100% O2
Thousands of fibrils that are distributed thoughout the ventricles, which represent the end of the cardiac conduction system, are called the
- Bundle branches
- Internodal pathways
- Pukinje fibers
- Cardiac myocytes
During the attempted resuscitation of a man in V-fib cardiac arrest, your protocols call for the administration of 1.5 mg/kg of lidocaine. You have prefilled syringes of lidocaine in a concentration of 100 mg/5 ml. The patient weighs 180 lbs. How many mL will you administrer.
- 5.5
- 6.2
- 6.5
- 6.8
If a burn patient presents with a hoarse voice and states "I'm cold" your most immediate concern should be
- Hypothermia
- Burn shock
- Inhalation injury
- Cyanide toxicity
no image
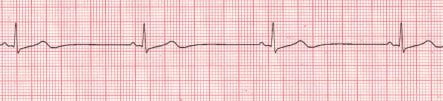
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Asystole
- 3rd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Inferior MI
- 1st Degree Heart Block
- Failure To Capture
- 2nd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Anterior MI
- Torsades
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Paced Rhythm
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
What drug is an antianginal, calcium blocker, antiarrhythmic, and vasodilator?
- Atropine
- Nitroglycerin
- Verapamil
- Nipride
The signs of epiglottitis are:
- Fever and chills
- Dysphagia and drooling
- Rales and dyspnea
- Aphasia and fever
During the third collision in a motor vehicle crash
- Hollow abdominal organs rupture upon impact
- The persons abdomen collides with the steering wheel
- Rapid deceleration propels an unrestrained person forward
- Abdominal organs shear from their points of attachment
An electrical impulse is slightly delayed at the AV node so that the
- Bundle of His can depolarize fully
- Ventricles can contract completely
- Primary cardiac pacemaker can reset
- Atria can empty into the ventricles
Following a spinal injury, a patient presents with abdominal breathing and use of the accessory muscles in the neck. This suggests injury at or above
- C1-c2
- C3-c4
- T1-t4
- T2-t5
Chronotropic means:
- Time related
- Nothing
- Electrolytic
- Force related
With regard to stroke volume, a healthy heart
- Has a relatively fixed stroke volume
- Has an average stroke volume of 40 ml
- Can double stroke volume if demand is high
- Can easily increase stroke volume by 50%
You reassess your patient after administering a medication via the IV bolus route and note that his clinical condition is unchanged. What is the least likely cause of the patient's unchanged condition
- The patient may require another dose of the same drug
- The dose was too low for the patient's clinical condition
- The IV tubing was occluded proximal to the injection
- You diluted the bolus by following it with a 20 mL saline flush
The purpose of estimating a patient's TBSA burns in the prehospital setting is to
- Obtain an accurate calculation of how severe the patient's burns are
- Determine whether the patient should be transported via helicopter
- Ascertain how much IV fluid the patient should receive during transport
- Help the paramedic determine the most appropriate destination hospital
The best possible score for a Glasgow coma scale is:
- Eye opening 6; verbal response 5; motor response 4
- Eye opening 5; verbal response 5; motor response 5
- Eye opening 4; verbal response 5; motor response 6
- Eye opening 3; verbal response 3; motor response 5
An essential, yet often overlooked, component of the EMS system is
- The QI process
- The public
- The medical director
- The training officer
With regard to thermal burn injury, the zone of coagulation
- May undergo necrosis within 24-48 hours after the burn
- Surrounds the central part of the burn and is often inflamed
- Is the area least affected by the burn and will likely recover
- Is the central part of the burn and suffers the most damage
A ruptured tympanic membrane
- Commonly results in permanent hearing loss
- Is characterized by CSF leakage from the ears
- Commonly leads to an infection of the middle ear
- Is extremely painful but typically heals spontaneously
no image
.jpg)
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Asystole
- 3rd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Inferior MI
- 1st Degree Heart Block
- Failure To Capture
- 2nd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Anterior MI
- Torsades
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Paced Rhythm
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
When administerd, epinephrine produces a/an _________effect
- Anticholineric
- Sympathomimetic
- Sympatholytic
- Parasympatholytic
Which of the following statements regarding scald burns is most correct
- Once hot liquids come in contact with clothing, heat is rapidly dissipated
- Scald burns often cover large surface areas because liquids spread quickly
- Scald burns caused by grease or oil are typically limited to the epidermis
- Scald burns are less commonly seen in pediatric patients that adult patients
What is an adult dose of Epinephrine in cardiac arrest?
- 2mg
- 1mg
- 2.5mg
- 1mg/kg
EMS providers can have the most positive impact on mortality and morbity from abdominal trauma by
- Recognizing the need for rapid transport
- Initiating fluid resuscitation in the field
- Contracting medical control immediately
- Performing a careful abdominal assessment
no image
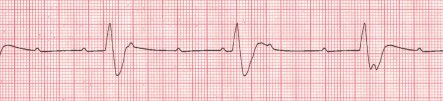
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Asystole
- 3rd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Inferior MI
- 1st Degree Heart Block
- Failure To Capture
- 2nd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Anterior MI
- Torsades
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Paced Rhythm
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
A person who is exposed to cement
- Typically only experiences burns to the epidermal layer because calcium oxide is a weak chemical
- Often does not experience a burn unless he or she is exposed to the cement for longer than 2 hours
- May not notice a skin burn for hours because cement penetrates through clothing and reacts with sweat
- Experiences immediate pain and inflammation to the area because of the calcium oxide in the cement
Unlike chemical burns, radiation burns
- Generally extended into the dermal layer
- May appear hours or days after exposure
- Are typically confined to the epidermis
- Are immediately apparent after exposure
no image
.jpg)
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Asystole
- 3rd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Inferior MI
- 1st Degree Heart Block
- Failure To Capture
- 2nd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Anterior MI
- Torsades
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Paced Rhythm
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
Drug legislation was instituted in 1906 by the
- Narcotics Act
- Cosmetics Act
- Pure Food and Drug Act
- Pharmacology Act
An injured patient's head should be secured to the long backboard only after
- You have placed padding under the shoulders
- His or her torso has been secured adequately
- Both of the legs are secured to the board properly
- A vest style immobilization device has been applied
Periumbilical ecchymosis is
- Commonly observed in the prehospital setting following blunt force trauma to the abdomen
- Referred to as cullen's sign and may take hours or days to develop following abdominal trauma
- Usually seen in conjunction with flank bruising and is highly suggestive of injury to the liver or spleen
- Also called grey turner's sign and manifests almost immediately following blunt abdominal trauma
A physiologic effect of the sympathetic nervous stimulation includes
- Dilation of the bronchioles
- Decreased conduction velocity
- A negative dromotropic effect
- Dilation of the blood vessels
Why do you want to give asprin to a patient with Acute Coronary Syndrome?
- Dilates arteries and veins, which redistributes blood volume and reduces ventricluar preload and afterload.
- Inhibits Thromoxane A2 platelet aggregation to reduce coronary reocclusion and recurrent events after fibrinolytic therapy.
- Dilates coronary arteries and vascular smooth muscle in veins, arteries, and arterioles.
- May limit ischemic myocardial injury, reducing the amount of ST segment elevation.
By definition, a massive hemothorax is characterized by
- Pulmonary injury with secondary myocardial injury
- 10% of circulating blood volume in the pleural space
- Cardiac arrest secondary to severe intrapleural bleeding
- More than 1,500 mL of blood within the pleural space
I should always label patient specimens at the printer where the labels print off, verifying the name and date of birth with the computerized record and the nurse.
- True
- False
If intubation of a burn patient becomes necessary, you should avoid cutting the ET tube down to make it shorter because
- This increases the risk of intubating the right mainstream bronchus
- Facial edema may cause tube dislodgement 2-3 days after the burn
- Drugs given via the ET tube will not adequately disperse in the lungs
- It may result in excessive volumes of air being delivered to the patient
The periumbilical area refers to the
- Space behind the navel
- External umbilical orifice
- Areas lateral to the umbilicus
- Area around the umbilicus
What is the cardiac output for an 80kg man who has a heart rate of 80 beats/min and a stroke volume of 60mL
- 4,800
- 5,200
- 6,000
- 6,400
no image
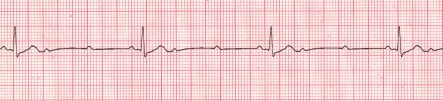
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Asystole
- 3rd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Inferior MI
- 1st Degree Heart Block
- Failure To Capture
- 2nd Degree Type 2 Heart Block
- Acute Anterior MI
- Torsades
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Paced Rhythm
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
While consulting with the attending physician at the receiving facility about a patient with symptomatic bradycardia, the physician orders you to administer 0.5 mg/kg of atropine to the patient. After recognizing that this is an inappropriate dose of atropine, you should
- Contact your medical director at once
- Ask the physician to repeat the order
- Refuse to administer the ordered dose
- Confirm the correct dose in your field guide
The spine
- Is the major structural component of the axial skeleton
- Is comprised of irregular bones that are all fused together
- Consists of 23 bones articulating to form the spinal column
- Provides support and strength for the appendicular skeleton
In contrast to secondary spinal cord injury, primary spinal cord injury occurs
- From progressive swelling
- At the moment of impact
- From penetrating mechanisms
- Within 24 hours of the injury
In a COPD patient the respiratory drive is triggered by?
- Hypocarbia
- Hypoxia
- Hypovolemia
- Hypercarbia
A 4 year old boy pulled a pot of boiling water off of the stove and experience partial thickness splash burns to his neck, anterior trunk, and both anterior arms. During your assessment, you not that the child is conscious, but is not crying. He is tachypneic, and tachycardic and his skin is cool and moist. Other than the burns, there are no other gross injuries. Which of the following statements regarding this scenario is most correct
- You should assist the child's ventilations and prepare to intubate his trachea
- An IV should be established and you should administer a 20 mL/kg bolus of D5W
- The child may be hypoglycemic and require assessment of his blood glucose level
- It is likely that this child's burn was intentionally inflicted and you should report it
A patient with a dysconjugate gaze following an occular injury
- Most likely has a concomitant basilar skull fracture
- Should have ice applied to the eyes to prevent blindness
- Has discoordination between the movements of both eyes
- Should be treated by irrigating both eyes for 20 minutes
Administering a drug that possesses a positive chronotropic effect will have a direct effect on
- Stroke volume
- Blood pressure
- Cardiac output
- The heart rate
Please select all that apply.When I am working with the Discharge Nurse, I know that I am to:
- Help in the areas with patient care, if there are no pending discharges.
- Call the Charge Nurse, Shift Coordinator or Manager to help if we get behind.
- Remove PIV's
- Take Vital Signs, if not taken within the last 60 minutes.
- Escort them to the waiting room, if necessary
- Answer all of the patient's questions
- Document Vital Signs in Cerner
You have dressed and bandaged a laceration to the arm of a 16 year old woman and are transporting her to the hospital. En route, the patient complains that her fingers are tingling. You touch her hand and not that it is cool. You should
- Readjust the bandage if needed and reassess distal neurovascular function
- Conclude that the laceration has probably severed a major nerve in her arm
- Elevate her arm, apply an icepack over the bandage, and reassess her hand
- Contact the receiving facility and have them place a neurosurgeon on standby
A 19 year old man fell approximately 20 feet, landing on a hard surface. Your assessment reveals that he is consious, is unable to move his lower extremities, and has pale, clammy skin above the level of his umbilicus. His respirations are 24 breaths/min and shallow, pulse rate is 50 beats/min and weak, and BP is 75/56mm Hg As your partner maintains stabilization of the patient's head, you perform a rapid trauma assesment, which reveals no obvious signs of hypovolemia. You should
- Apply high flow oxygen, attempt transcutaneous pacing to increase his heart rate, apply spinal motion restriction precautions, establish vascular access and administer a crystalloid bolus of 10-20 mL/kg, begin transport, and infuse dopamine at 2 mcg/kg/min en route
- Consider immediate intubation to protect his airway, apply spinal motion restriction precautions, apply warm blankets, begin transport, establish IV or IO access en route, and administer up to 4 liters of normal saline or lactated Ringer's solution to increase his BP and improve perfusion
- Assist ventilations as needed, apply spinal motion restriction precatutions, keep him warm, begin transport, establish vascular access en route, administer crystalloid boluses in 200 mL increments, consider atropine for his bradycardia, and infuse dopamine if his blood pressure is refractory to fluid boluses.
- Provide ventilatory assistance with a BVM device, establish immediate vascular access and infuse normal saline wide open, apply spinal motion restrictions, administer 1 mg of atropine to increase his heart rate above 60 beats/min, begin transport, and perform transcutaneous pacing en route if he remains bradycardic
The P wave represents
- SA nodal discharge
- Atrial depolarization
- A depaly at the AV node
- Contraction of the atria
What is your dose for Adenosine?
- 6mg, 6mg,12mg
- 6mg, 12mg, 6mg
- 12mg, 12mg, 6mg
- 6mg, 12mg, 12mg
Burn shock is caused by
- A massive infection that occurs when microorganisms breach burned skin
- Renal failure secondary to excess myoglobin production from burned muscle
- Fluid loss across damaged skin and volume shifts within the rest of the body
- Acute dehydration, and it commonly manifests within 30 minutes after the burn
The following describes a Schedule ____ drug: High abuse potential; may lead to severe dependence; accepted medical indications.
- I
- II
- III
- IV
The force or forces that cuased an injury define the:
- Nature of illness
- Chief complaint
- Mechanism of injury
- Primary illness
You and your partner are transporting a severely burned patient from a community hospital to a burn specialty center. The patient, a 33 year old, 110 lb woman, has partial and full thickness burns that cover approximately 55% of her body. She has two large bore IV lines in place, is intubated, and is on a cardiac monitor. According to the parkland formula, how much normal saline should she receive in 30 minutes
- 340mL
- 355mL
- 370mL
- 395mL
Which of the following statements regarding the liver is most correct
- The liver is the largest hollow organ in the abdomen and is responsible for producing and storing bile
- The liver is a relatively avascular organ that is uncommonly injured during blunt abdominal trauma
- The liver is a solid organ that lies in the right upper abdominal quadrant and detoxifies the blood
- The liver is partially protected by the left lower ribcage and serves the function of filtering bacteria from the blood
Which layer of the blood vessel is made up of elastic fibers and muscle, and provides for strength and contractility
- Tunica media
- Tunica intima
- Tunica adventitia
- Arterial lumen
According to the rule of nines, an adult man with partial and full thickness burns to his head, face and anterior chest has burns to __% of his TBSA
- 18
- 27
- 36
- 45
Please select all of the following that apply. Preparing a room for a suicidal patient includes;
- Changing the sheet to a paper sheet
- Changing the patient gown to a paper gown
- Insuring all oxygen tanks are removed from under the cart
- Removing any hazards from the room that may cause harm to the patient
- Always locking the door when the patient is in there, no matter what
- Always locking the door when the patient is in there, no matter what
- Always locking the door when the patient is in there, no matter what
_____ trauma patients have very minor injuires and can wait for treatment or they are dead and no treatment is necessary.
- Priority-1
- Priority-2
- Priority-3
- Priority-4
Signs of neurogenic shock include all of the following except
- Bradycardia
- Flushed skin
- Diaphoresis
- Hypothermia
______ is the preferred antihypertensive for the management of pregnancy induced hypertension.
- Coreg
- Apresoline
- Captopril
- Nifedipine
You have just completed spinal immobilization of a hemodynamically stable patient with a possible spinal injury. Prior to moving the patient to the ambulance, it is most important to
- Start an IV of normal saline in case the patient deteriorates
- Apply a cardiac monitor and obtain a full set of vital signs
- Performed a detailed physical exam to detect other injuries
- Reassess pulse, motor, and sensory functions in all extremities
As the contents exit the stomach, they first pass through the
- Pylorus
- Duodenum
- Gallbladder
- Cardiac sphincter
Following blunt trauma to the face, a 30 year old man presents with epistaxis, double vision and an inability to look upward. You should be most suspicious of
- Traumatic conjunctivitis
- An orbital blowout fracture
- Traumatic retinal detachment
- Fracture of the cribiform plate
Uncompensated shock produces which of the following:
- Pre-capillary and post-capillary sphincter dilation
- Pre-capillary sphincter relaxation and post-capillary sphincter contraction
- Pre-capillary sphincter contraction and post-capillary sphincter
- A pre-capillary and post-capillary sphincter contraction
A 30 year old man presents with jaw and neck stiffness and fever. During your assessment, he tells you that he cut his hand on a piece of metal about a week ago. You should be most suspicious that this patient has
- Tetanus
- Meningitis
- A viral infection
- A staph infection
Alkali or strong acid burns to the eye should be irrigated for an absolute minimum of ______minutes
- 10
- 15
- 20
- 30
What do you want to avoid during CPR?
- Hyperventilation
- Hypoventilation
- Breaking the ribs
- Shocking the Patient
When treating a patient with bradycardia, what is your first initial action according to Bradycardia algorithm?
- Establish IV Access
- Assist Breathing
- Give them Oxygen
- Maintain Patent Airway
The amount of blood that is pumped out by either ventricle per minute is called
- Ejection fraction
- Cardiac output
- Stroke volume
- Minute volume
Autoregulation is most accurately defined as
- Reflex bradycardia that occurs secondary to systemic hypertension
- An increase in mean arterial pressure to maintain cerebral blood flow
- The forcing of CSF into the spinal cord as intracranial pressure increases
- A decrease in cerebral perfusion pressure that reduces intracranial pressure
A patient with full thickness burns surrounded by areas of superficial and partial-thickness burns should be treate with all of the following except
- Analgesia
- High flow oxygen
- Moist dressings
- Sterile burn pads
The drug name found in the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) is its
- Official name
- Chemical name
- Generic name
- Trade name
Atrial kick is most accurately defined as
- The blood that flows passively into the ventricles
- Pressure on the atrioventricular valves during ventricular contraction
- An attempt of the atria to contract against closed valves
- 20% of ventricular filling caused by atrial contraction
When assessing the severity of a traumatic brain injury, the single msot important assessment parameter is the patient's
- Initial GSC score
- Blood pressure
- Level of consciousness
- Response to verbal stimuli
When doing CPR, how many compressions do you give each minute?
- 30
- 60
- 90
- 100
What is your first line for treating Acute Pulmonary Edema?
- Fluids, Blood Transfusion, oxygen, transport
- Oxygen, Nitro, Lasix, Morphine
- Oxygen, Fluids, Lasix, Valium
- Oxygen, Nitro, Lasix, Morphine, Fluids, Atropine
When an unrestrained passenger's head strikes the windshield of a motor vehicle following rapid deceleration
- The anterior portion of the brain sustains stretching or tearing injuries and the posterior portion of the brain sustains compression injuries
- The head falls back against the headrest or seat and the brain collides with the rear of the skull, resulting in direct injury to the occipital lobe
- The brain initially strikes the rear of the skull, resulting in direct bruising, and then rebounds and strikes the front part of the skull
- Compression injuries occur to the anterior portion of the brain and stretching or tearing injuries occur to the posterior portion of the brain
Cardiac output is the product of ____ and ____.
- HR and Disastolic pressure
- HR and Stroke Volume
- HR and EF
- Diastolic and Systolic pressure
Professional organizations that help shape the public perception of EMS include all of the following except:
- NASAR
- NAEMSE
- NAEMSP
- NFPA
Most lighting related injuries occur when the victim
- Experiences a direct hit while standing in a large open area
- Is talking on a phone and a utility pole is truck by lighting
- Is attempting to escape an oncoming thunderstorm by running
- Receives a splash effect after lighting strikes a nearby object
Which is the best way to lower a patient?
- Horizontal
- It doesn't matter
- Inverted
- Vertical
The proper rate for rescue breathing for an adult is:
- 8 breaths/minute
- 12 breaths/minute
- 5 breaths/minute
- 20 breaths/minute
What do you want to avoid giving a stroke patient?
- Thiamine
- D 5 W
- Excessive fluid loading
- D 5 W and excessive fluid loading
While assisting the RN, you understand the following interventions/assessments are indicated for stroke patients receiving alteplase?
- NPO until dysphagia screen completed
- Vital Signs every 15 minutes x 2 hours
- Neuro Checks every 15 minutes x 2 hours
- All of the above
The joint action of two drugs where the combined effect is greater than the sum of their individual effect is called:
- Antagonism
- Synergism
- Idiosycrasy
- Potentiation
Which is the most important in evaluating a patient with all illness causing abdominal pain?
- Appearance of the patient
- Palpitation
- Vital signs
- Patient history
Which of the following statements regarding partial-thickness burns is most correct
- Partial thickness burns are usually extremely painful for the patient
- They are difficult to distinguish from a superficial burn in the field
- The majority of partial thickness burns are caused by an open flame
- Is the central part of the burn and suffers the most damage
An open pneumothorax causes ventilatory inadequacy when
- Positive pressure created by expiration forces air into the pleural space
- The heart stops perfusing the lung on the side of an open chest injury
- Negative pressure created by inspiration draws air into the pleural space
- The glottic opening is much larger than the open wound on the chest wall
A 76-year-old male is brought to the ED because of severe abdominal pain. He tells you, "it feels like someone is ripping me apart." The pain began 45 minutes ago and he rates the intensity as 10/10. He has a PMH of hypertension, for which he takes a duretic and a beta blocker. his skin is cool and diaphoretic. Vital Signs are: B/P 88/68, HR 88, RR 24, SPO2 94%. It would be most appropriate to call him a:
- Cardiac One
- Trauma 2
- Here Now, Vascular One
- Medical Alert
What type of thermal burn is most commonly associated with inhalation injury
- Steam burns
- Flame burns
- Scald burns
- Arc burns
Damage to the kidneys follows an electrical injury
- Is caused by excess serum potassium levels
- Occurs when damaged muscle produces myoglobin
- Can be prevented with boluses of lactated ringers
- Is the result of electricity passing through the kidneys
The diaphragm
- Is an accessory muscle used during respiratory distress
- Works in conjunction with the sternum during inspiration
- Forms a barrier between the thoracic and abdominal cavities
- Creates positive intrathoracic pressure when it increases in size
If a knife is impaled in the neck
- A cricothyrotomy may be required to establish a patent airway
- It should be removed in case the airway becomes compromised
- You should stabilize the object in place, regardless of its location
- It should be shortened to facilitate proper airway management
The severity of a thermal burn correlates directly with
- The body's ability to effectively dissipate significant heat energy and the patient's general state of health
- The presence of any underlying medical problems, the duration of exposure, and the temperature of the heat source.
- The duration of exposure, the physical size of the patient, and the presence of concomitant traumatic injuries.
- The temperature of the heat source of the heat source, amount of heat energy possessed by the object or substance and the duration of exposure
How often can you administer Epinephrine?
- 2-5min
- 3-7min
- 1-3min
- 3-5min
Stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system causes all of the following effects, except
- Negative inotropy
- Increased salsivation
- Dilation of the pupils
- Negative chronotropy
Phosphorus is found in_______ and burns when exposed to ________
- Fireworks,air
- Oven cleaner, water
- Drain cleaner, air
- Battery acid, water
The ability of the heart to vary the degree (force) of its contraction without stretching is called
- Contractility
- Chonotropy
- Automaticity
- Frank-starling effect
A 31 year old male is involved in a MVA. Vital signs are 90/68, 100, and 40. Trachea is deviated to the right, breath sounds are absent on the left, hyperresonance is noted on the left side on percussion. What is mostly likely the problem?
- Simple pneumothorax
- Pericardial tamponade
- Hemothorax
- Tension pneumothorax
Which of the following statements regarding carbon monoxide poisoning is most correct
- Never rule out CO poisoning because of the absence of cherry red skin
- The most common symptom of CO poisoning is chest pressure
- CO results in systemic hypoxia by disintegrating red blood cells
- Hyperbaric therapy is beneficial only if CO levels are above 40%
You are caring for a man with a chemical burn to both eyes. The patient, who has contact lenses in place, is in severe pain and tells you that he can't see. Proper care for this patient includes
- Carefully removing his contact lenses, flushing both eyes for at least 20 minutes, and transporting with continuous eye irrigation
- Leaving his contact lenses in place to avoid further injury and transporting at once with irrigation of both eyes performed en route
- Removing his contact lenses, covering both eyes with moist, sterile dressings, administering a narcotic analgesic, and transporting
- Asking the patient to remove his contact lenses, irrigating both eyes for no more than 10 minutes, covering both eyes with sterile dressings, and transporting
The patient in the trauma room had a chest tube inserted for a hemathorax. You notice the patient has become short of breath and his SPO2 is decreasing. This could mean that:
- The tubing is kinked
- There is a clot obstructing the chest tube
- There is a dependent, fluid filled, loop in the tubing
- All of the above
Death following a head injury is almost always the result of
- An epidural hematoma
- Trauma to the brain
- Airway compromise
- Spinal cord transection
____ is a project published in 1996 and supported by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.
- Emergency Medical Services for Children (EMS C)
- EMS Agenda For The Future
- White Paper
- OPALS
A 19 year old woman fell from a secondary window and landed on her head. She is unconscious with a blood pressure of 148/94 mm Hg, heart rate of 58 beats/min , and irregular respirations of 8 breaths/ minute. Further assessment reveals blood draining from her nose and bilaterally dilated pupils that are slow to react. In addition to employing full spinal precautions, the most appropriate treatment for this patient involves
- Hyperventilating her with a BVM at a rate of 20 breaths/min, starting two large bore IVs applying a cardiac monitor, administering 5 mg of valium to prevent seizures, and transporting to a trauma center.
- Preoxygenating her with a BVM and 100% oxygen for 2-3 minutes with a BVM , transporting immediately, starting at least one large bore IV en route, and obtaining her glasgow coma scale score
- Intubating her trachea after preoxygenating her for 2-3 minutes with a BVM, transporting immediately, starting at least one large bore IV en route, applying a cardiac monitor, and performing frequent neurologic assessments
- Applying oxygen via nonrebreathing mask, covering her with blankets, starting an IV of normal saline set to keep the vein open, applying a cardiac monitor, initiating transport, and monitoring her pupils while en route to the hospital
The brief pause between the P wave and the QRS complex represents
- Depolarization of the inferior part of the atria
- The period of time when the atria are repolarizing
- Full dispersal of electricity throughout both atria
- A momentary conduction delay at the AV junction
If you have SVT with aberrancy's what medication do you administer?
- Amiodarone
- Adenosine
- Atropine
- Diazepam
You are helping provide care for a patient while the Primary Nurse is giving bedside report on a patient with an EVD. A patient with an External Ventricular Drain should:
- Have the EVD placed at the correct zero reference level
- Have fluctuation in the tubing
- Have all stopcocks open to the drain, except during transport
- All the above
Vasoconstriction occurs following stimulation of
- Beta 1 receptors
- Beta 2 receptors
- Alpha receptors
- Alpha and beta receptors
When a patient reports being a victim of domestic violence, after notifying the primary nurse, I know to notify the:
- Forensic Nurse
- Physician
- Secretary
- Shift Coordinator
Because of its anatomical position in the retroperitoneum, it typically takes high energy force to damage the
- Liver
- Spleen
- Stomach
- Pancreas
Management of acute brain injury is aimed at decreasing secondary brain injury. Which is not an appropriate intervention for a patient with an acute brain injury?
- Maintaining neutral body alignment
- Maintaining normathermia
- Increasing environmental stimuli
- Elevating the head of the bed 30 degrees, unless contraindicated
At what temp do you have Mild Hypothermia?
- 93.2-96.8 degrees F
- 86-93.2 degrees F
- 80-86 degrees F
- 94-97.8 degrees F
When auscultating the lungs of a patient with early pulmonary edema, you will most likely hear
- Inspiratory rhonchi to the bilateral apices of the lungs
- Crackles in the bases of the lungs at the end of inspiration
- Faintrhonchi to all lung fields on inspiration and expiration
- Wheezing during inspiration
The term _____ refers to the conduct or qualities that characterize a practicioner in a particular field or profession.
- Licensure
- Registration
- Professionalism
- Certification
What joules will you use to shock a 37-yr-old male patient who weighs 200 lbs?
- 200 joules
- 300 joules
- 360 joules
- 2-4 joules/kg
A 19 year old female comes to front triage, Alert and Oriented, with a GSW to her upper arm & right shoulder, you know this patient should be called a:
- Medical Alert
- Trauma 1
- Trauma 2
- Trauma 3
When managing the airway of an unresponsive patient with serious anterior neck trauma and inadequate breathing, you should
- Apply a cervical collar and perform intubation immediately
- Ventilate the patient with an oxygen powered ventilation device
- Give oxygen via nonrebreathing mask and apply a pulse oximeter
- Secure manual in-line stabilization of the cspine, assist ventilations with a BVM, and prepare to intubate
Beta receptor stimulation results in all of the following effects , except
- Positive cardiac inotropy
- Positive cardiac chronotropy
- Vascular smooth muscle contraction
- Relaxation of bronchiole smooth muscle
A 24 year old woman was struck by lightning. Bystanders moved the patient to an area of safety but did not provide any other care before your arrival. Your initial assessment reveals that the patient is pulseless and apneic. After performing CPR for 2 minutes, you assess her cardiac rhythm, which reveals asystole. After requesting a backup paramedic unit, the most appropriate treatment for this patient involves
- Instructing your partner to resume one rescuer CPR, establishing an IV of normal saline, and reassessing her cardiac rhythm in 5 minutes
- Continuing CPR, providing full spinal precautions, intubating her trachea, and ventilating her at a rate of 20-24 breaths/min
- Performing adequate BLS, following standard ACLS protocol, and considering terminating your efforts if asystole persists after 10 minutes
- Continuing CPR, protecting her spine while ventilating, reassessing her cardiac rhythm after 2 minutes of CPR, and defibrillating if necessary
Stimulation of alpha and beta receports affects the
- Heart only
- Heart and blood vessels
- Blood vessels and the lungs
- Heart, lungs, and blood vessels
During an explosion, a 42 year old construction worker sustained a large laceration to the lateral aspect of his neck when he was struck by a piece of flying debris. The patient is conscious, but complains of difficulty hearing. In addition to protecting his spine, you hould be most concerned with
- Administering high flow oxygen via non rebreathing mask as soon as possible
- Covering the laceration with an occlusive dressing and controlling the bleeding
- Carefully examining his ear to determine if his tympanic membrane is ruptured
- Applying a bulky dressing to the laceration and securing it firmly with a bandage
Which drug must be given cautiously to patients currently taking digitalis?
- D50
- Diazepam
- Epinephrine
- CaCl
Which drug is contraindicated in asthma patients?
- CaCl
- Digitalis
- Inderal
- Epinephrine
A pure alpha agent
- Causes marked vasoconstriction
- Has a direct effect on the heart rate
- Causes moderate bronchoconstriction
- Decreases the blood pressure by dilating the blood vessels
Decerebrate and decorticate posturing is an indication of:
- Diffuse cranial injury
- Cerebral focal cortex lesions
- Spine injury
- Seizure
Your 25 year old female patient is complaining of vaginal discharge and abdominal pain which increased with intercourse. The patient relates that she may have been exposed to gonorrhea. The patient is most likely suffering from:
- Uterine rupture
- Ectopic pregnancy
- PID
- AIDS
Which of the following is a calcium channel blocker?
- Verapmil
- Isoptin
- Calan
- All of the above
The act of receiving a comparable certification or licensure from another state or agency is known as
- Registration
- Reciprocity
- Regulation
- Reciprocation
EMS trauma care generally evolves following
- Studies and scientific reviews
- Conflicts
- Medical consortiums
- Quality improvement reviews
The pressure within the right ventricle is
- Less than the pressure within the right atrium
- One fourth of the pressure within the left ventricle
- Nearly equal to the pressure within the left ventricle
- Three times greater than the pressure in the left ventricle
What prevents the backflow of blood during ventricular contraction
- The aortic valve
- Semilunar valve
- The pulmonic valve
- Atrioventricular valve
The APGAR score evaluates:
- Pulse, reflex ability, appearance, BP
- Pulse, respirations, BP, activity, color
- Pulse, respirations, activity, color, grimace
- BP, pulse, gestation, color, respiration
Which of the following factors does not contribute to the extent of injury from a gunshot wound to the abdomen
- Size of the patient
- Profile of the bullet
- Trajectory of the bullet
- Distance the bullet traveled
Uncompensated shock is evidenced by:
- Rising temperature
- Falling blood pressure
- Cold, clammy skin
- Rising pulse rate
A complete spinal cord injury to the upper cervical spine
- Results in quadriplegia but the patient usually retains his or her ability to breathe spontaneously
- Is not compatible with life and results in immediate death due to cardiopulmonary failure
- Will result in permanent loss of all cord mediated functions below the level of the injury
- Results in neurologic dysfunction that is considered to be permanent if it lasts longer than 24 hours
When assessing a patient with maxillofacial trauma, it is most important to
- Gently palpate the maxilla, mandible, and zygoma to elicit creipitus
- Protect the cervical spine and monitor the patient's neurologic status
- Apply a cervical collar and determine if the patient has visual disturbances
- Have the patient open his of her mouth and assess for dental malocclusion
What does the T wave represent on the ECG?
- Ventricular depolarization
- Atrial depolarization
- Atrial repolarization
- Ventricular repolarization
The visceral pericardial layer
- Comprises the pericadial sac itself
- Is attached directly to the diaphragm
- Is the outermost layer of the pericardium
- Adheres to the heart and forms the epicardium
You respond to an industrial plant for a 42 year old man with a chemical burn. Upon arrival at the scene, you find the patient to be ambulatory. He tells you that he was moving some bags of dry lime when one of the bags broke and spilled lime all over him. After donning the appropriate personal protective equipment, you should
- Remove his clothing, brush as much of the lime off him as possible, and flush the affected areas with copious amounts of water
- Avoid brushing any of the lime from his skin as this may cause additional injury and flush his entire body with water for 30 minutes
- Remove his clothing, carefully brush the lime away from his skin, but avoid flushing with water as this will likely increase burn severity
- Remove all of his clothing, apply baking powder to neutralize the lime, and begin flushing his body with copious amounts of sterile saline
A 74 year old man experienced partial and full thickness burns to his arms and chest resulting from a fire that started after he fell asleep while smoking. The patient's son, who arrived at the scene shortly after you, states that his father has congestive heart failure, rheumatoid arthritis, and artrial fibrillation. In addition to administering supplemental O2, it is most important for you to
- Avoid narcotic analgesics because of his medical history
- Auscultate his breath sounds before administering IV fluids
- Obtain a 12 lead ECG to assess for signs of cardiac ischemia
- Apply cold, moist dressings to his burns to provide pain relief
Which of the following is not a sight of potential injury when the aorta is subjected to shearing forces during rapid deceleration
- Anulus
- Coronary sinus
- Aortic hiatus
- Ligamentum arteriosum
A 22 year old man was struck in the forehead by a softball. He is conscious and alert, but comlains of a severe headache. Your assessment reveals a large hematoma to his forehead. His vital signs are stable and his breathing is adequate. You should
- Apply firm manual pressure to the hematoma to reduce internal bleeding
- Place him in a sitting position and apply a chemical heat pack to his head
- Apply an icepack to the hematoma and monitor his level of consciousness
- Start an IV of normal saline and administer 2 mg of morphine for the pain
As the body ages, the intervertebral discs
- Calcify and become more rigid
- Enlarge and result in increased height
- Are not able to protect the spinal cord
- Lose water content and become thinner
Isolated rib fractures may result in inadequate ventilation because
- The patient often purposely limits chest wall movement
- Most rib fractures cause paradoxical chest wall movement
- The pain associated with the fracture causes hyperventilation
- Preferential use of the intercostal muscles reduces tidal volume
The eighth, ninth, and tenth ribs are indirectly attached to the sternum by the
- Manubrium
- Angle of louis
- Costal cartilage
- Suprasternal notch
Approximately 20 minutes after starting an IV on a 40 year old man, he begins complaining of a backache and chills. You should most be suspicious of
- An air embolus
- An allergic reaction
- Circulatory overload
- A pyrogenic reaction
Anatomically, the abdominal cavity extends from the
- Fifth rib to the pelvis
- Umbilicus to the pelvis
- Diaphragm to the pelvis
- Nipple line to the diaphragm
______ drug sources may provide alternative sources of medications to those found in nature, or they may be entirely new medications not found in nature.
- Plant
- AnimalAnimal
- Synthetic
- Mineral
A 52 year old man sustained superficial and partial thickness burns to his left arm approximately 15 minutes ago when he opened the radiator cap on his car. He is conscious, alert, and in severe pain. His BP is 138/76 mm Hg, pulse is 110 beats/min and strong, respirations are 22 breaths/min and regular, and his oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. He denies any other injuries. Initial management for this patient involves
- Applying ice to the burn to provide immediate pain relief
- Applying cool, wet dressings to the burn and elevate his arm
- Starting an IV of normal saline and administering 2 mg of morphine
- Administering oxygen and applying an anesthetic cream to the burn
In contrast to arteries, veins
- Do not contain valves that prevent backflow of blood
- Have less capacity to increase the size of their diameter
- Are more likely to distend when exposed to back pressure
- Operate on the high-pressure side of the circulatory system
Compared to beta radiation particles, alpha radiation particles
- Have minimal penetrating energy
- Easily pass through solid materials
- Are able to travel much farther in air
- Are not dangerous if they are ingested
Maintaining a complete and accurate written patient care report is essential to:
- Research efforts
- The flow of patient information
- The quality improvement of EMS systems
- All of the above
You are dispatched to a residence for a man who has cut his hand with a chainsaw. Upon arriving at the scene, your first action should be to
- Immediately gain access to the patien
- Apply gloves, a gown and facial protection
- Determine if air medical transport is available
- Carefully assess the scene for safety hazards
Because they can thicken the broncial secretions you should not use ____ in patients with asthma
- Mucolytics
- Antitussives
- Antihistamines
- Antiarrhythmics
If you have a hypothermic patient what is the first thing you do?
- Check ABC's
- Start CPR
- Check Core Temp
- Remove all wet garments
_____ are rules or standards that govern the conduct of members of a particular group or profession.
- Ethics
- Morals
- Etiquette
- Protocols
Dysrhythmias following a myocardial contusion are usually secondary to
- Excess tachycardia that accompanies the injury
- Damage to myocardial tissue at the cellular level
- Aneurysm formation caused by vascular damage
- Direct damage to the vasculature of the epicardium
The ________ is a continuation of the central nervous system and exits the skull through the ________
- Vagus nerve, spinal cord
- Spinal cord, foramen magnum
- Brain stem, verebral foramen
- Medullar, cauda equina
Fractures of the lower rib cage should make you most suspicious for injuries to the
- Liver or spleen
- Urinary bladder
- Ascending aorta
- Kidneys or pancreas
Where is the Macintosh blade inserted during intubation?
- Epiglottis
- Trachea
- Vallecula
- Larynx
When blood is released into the peritoneal cavity
- The abdomen almost immediately becomes grossly distended
- It is most often the result of blunt force trauma to the pancreas
- Blood pressure falls with as little as 500 mL of internal blood loss
- Nonspecific signs such as tachycardia and hypotension may occur
A motorcycle of football helmet should be removed if
- The patient complains of severe neck pain and the helmet fits snugly
- You are going to transport the patient to a medical treatment facility
- The patient is breathing shallowly and access to the airway is difficult
- You are properly trained in the technique, even if you are by yourself
All of the following are components of the communications network of a regional EMS system except:
- Citizen access
- Single control center
- Operational communications capabilitie
- Medical direction
- Communications hardware and software
The effect on the velocity of electrical conduction is referred to as the _________effect
- Inotropic
- Dromotropic
- Chronotropic
- Conductivity
A skier wiped out while skiing down a large hill. He is conscious and alert and complains of being very cold, he also complains of neck stiffness and numbness and tingling in all of his extremities. A quick assessment reveals that his airway is patent and his breathing is adequate. You should
- Perform a detailed neurologic exam and carefully palpate his neck
- Apply a cervical collar and start and IV line with warm normal saline
- Immobilize his spine a quickly move him to a warmer environment
- Administer oxygen and perform a focused history and physical exam
In contrast to the right side of the heart, the left side of the heart
- Drives blood out of the heart against the relatively high resistance of the systemic circulation
- Is a high-pressure pump that sends blood through the pulmonary circulation and to the lungs
- Is a relatively low pressure pump that must stretcher its walls in order to force blood through the aorta
- Drives blood out of the heart against the relatively low resistance of the pulmonary circulation
Traumatic injuries to the aorta are most commonly the result of
- Shearing forces
- Rear-end collisions
- Penetrating trauma
- Motorcycle crashes
Before applying a PASG you must:
- Start an IV
- Assess lung sounds
- Insert an oral airway
- Measure the legs of the patient
The death which occurs at the moment the heart stops is:
- Irreversible death
- DRT
- Biological death
- Clinical death
The sinoatrial node
- Cannot depolarize faster than 100 times/min
- Will normally outpace any slower conduction tissue
- Functions as the heart's secondary pacemaker
- Has an intrinsic firing rate of 40-60 beats per minute
What leads will you see Lateral problems in?
- Leads I, aVL, aVF, V5
- Leads I, aVL, V2, V1
- Leads I, aVL, V5, V6
- Leads I, aVL, aVR, V4
A 22 year old man was kicked in the abdomen several times during an assault. Your initial assessment reveals that he is responsive only to pain, has poor respiratory effort, and a pulse rate that is rapid and weak. Further assessment reveals abrasions with minimal bleeding to his upper extremities and face, no other gross external bleeding is present. You should
- Protect his spine, insert a nasal airway, assist ventilations with a BVM and 100% O2. keep him warm and elevate his legs, transport at once, and establish vascular access en route to a trauma center
- Perform immediate endotracheal intubation, apply a cervical collar, establish two large bore IV lines and give a fluid bolus at the scene, apply warm blankets, and transport expeditiously to a trauma center
- Apply high flow oxygen via nonrebreathing mask, apply blankets, elevate his lower extremities 12 inches, insert bilateral intraosseous catheters, deliver a 500mL fluid bolus, and begin transport to a trauma center
- Insert an oral airway, hyperventilate him with a BVM at 24 breaths/min, keep him warm and elevate his legs, transport at once, and establish at least one large bore IV line of normal saline while en route to a trauma center
The least significant complication associated with damage to the skin following a burn injury is
- Decreased melanin granules
- Disturbances in fluid balance
- Difficulty with thermoregulation
- Susceptibility to bacterial invasion
Anaphylaxis following an insect sting is treated with:
- Epinephrine
- Aminophylline
- Morphine sulfate
- Benadryl
Gross hematuria and suprapubic pain following a pelvic injury is most indicative of injury to the
- Ureters
- Urethra
- Bladder
- Kidney
While attempting to start an IV on a patient with large proturuding veins, you note that the vein rolls from side to side during your cannulation attempt. The best way to remedy this situation is to
- Apply downward manual traction below the venipuncture site to stabilize the vein in position.
- Apply the constricting band to a distal location
- Use a through the needle IV catheter in order to gain better control over the rolling vein
- Place a chemical heat pack over the vein for 10 minutes in order to decrease movement of the vein
The proprietary name of a drug, such as Valium, is the same as the
- Official name
- Chemical name
- Generic name
- Trade name
You have intubated an unconscious, apneic patient with a suspected spinal injury. After confirming proper ET tube placement and securing the tube, you should
- Request medical control authorization to give solu-medrol
- Ventilate at 10-12 breaths/min and monitor end-tidal CO2
- Maintain an end-tidal CO2 reading of greater than 45 mmHg
- Provide mild hyperventilation in case a head injury is present
no image
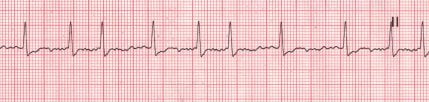
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Asystole
- 3rd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Inferior MI
- 1st Degree Heart Block
- Failure To Capture
- 2nd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Anterior MI
- Torsades
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Paced Rhythm
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
When transporting a patient with an EVD, the stopcock should be:
- Open to the collection chamber
- Closed to the collection chamber
The rate of adult compressions in CPR is:
- 5-2
- 80-100
- 100 plus per minute
- 15-1
What response is seen with Cushing's syndrome?
- Decreased production of cortizone
- Excess production of ACTH
- Excess production of oxytocin
- Decreased production of ACTH
Which of the following statements regarding the right side of the heart is most correct
- It receives blood exclusively from the venae cavae
- The right side of the heart is a low pressure pump
- It pumps against the high resistance of the pulmonary circulation
- The right side of the heart pumps blood through the pulmonary veins
An example of an anticholinergic drug used in the treatment of ashtma is:
- Atropine
- Ephedrine
- Proventil
- Beclovent
_____ trauma center provides the highest level of trauma care
- Level I
- Level II
- Level III
- Level IV
The layers of the heart, beginning with the outermost layer, are the
- Epicardium,myocardium,and endocardium
- Endocardium,epicardium, and myocardium
- Myocardium,epicardium, andendocardium
- Epicardium,ednocardium, and myocardium
What is a normal adults respiratory rate?
- 8-12 breaths/min
- 10-18 breaths/min
- 13-21 breaths/min
- 12-20 breaths/min
The major complications associated with hollow organ injury is
- Massive internal hemorrhage and profound shock
- Peritonitis caused by rupture and spillage of toxins
- Immediate death secondary to a massive infection
- Delayed treatment due to the absence of external signs
Cardiac output in influenced by
- Heart rate
- Stroke volume
- Heart rate and or stroke volume
- Ejection fraction and heart rate
The beta cells of the pancreas produce:
- Thyroxin hormone
- ACTH
- Anti-diuretic hormone
- Insulin hormone
What three things can you look for when doing a Cincinnati Pre-hospital Stroke Scale?
- Falls, Slurring, no smile, abnormal Speech
- Facial Droop, Arm Drift, Abnormal Speech
- Abnormal speech, talking really fast, screaming
- Facial Droop, Arm Drift, Drooling
A known diabetic who is unconscious, pale, clammy skin, with stable vital signs is suffering from:
- Insulin shock
- Acute AMI
- Diabetic coma
- CVA
In some people, congenitally weakened areas of the lungs may rupture causing:
- Alveolar pneumonia
- Pulmonary edema
- Spontaneous pneumothorax
- Hemothorax
Which of the following ECG waveforms represents ventricular depolarization
- T waves
- ST segment
- QRS complex
- U wave
The study of drugs and their interactions with the body is called
- Physiology
- Toxicology
- Pharmacology
- Pharmacopeia
Patient has high blood pressure in pregnancy:
- Uterine inversion
- Toxemia
- Preeclampsia
- Eclampsia
A woman is found lying in the street. When you ask her name, she moans incoherently. You report her level of consciousness as:
- Stuporous
- Conscious and disoriented
- Unconscious
- Semi-conscious
A 49 year old woman presents with a systolic BP of 70 mm Hg, a pulse rate of 130 beats/min and irregular, labored respirations of 28 breaths/min, and coarse crackles in her lungs. You should suspect _________shock and treat her with high-flow oxygen and____________
- Cardiogenic,dopamine
- Neurogenic,a beta blocker
- Hypovolemic, saline boluses
- Distributive, an antidysrhythmic
What are the T's when searching for and treating possible contributing factors?
- Toxins
- , Cardiac Tamponade
- , Tension Pneumothorax, Thrombosis, Trauma
During an emergency response, remember that _____ is your number one priority.
- Patient care
- Personal safety
- Documentation
- Medical direction
Intraperitoneal organs include all of the following, except the
- Panceas
- Stomach
- Small bowel
- Gallbladder
Many of the physiologic changes cause dby acute radiation syndrome
- Can be reversed if chemotherapy is administered within 24 hours
- Occur over time and will not be apparent in the prehospital setting
- Are a direct result of beta particles and are usually life threatening
- Manifest with lethal cardiac dysrhythmias and sudden cardiac arrest
The six rights of medication administration include the right
- Dose
- Time
- Route
- All of the above
A 22 year old man was struck in the forehead by a softball. He is conscious and alert, but complains of a severe headache. Your assessment reveals a large hematoma to his forehead. His vital signs are stable and his breathing is adequate. You should
- Apply firm manual pressure to the hematoma to reduce internal bleeding
- Place him in a sitting position and apply a chemical heat pack to his head
- Apply an icepack to the hematoma and monitor his level of consciousness
- Start an IV of normal saline and administer 2 mg of morphine for the pain
What heart valve prevents the backflow of blood into the right atrium?
- Aortic valve
- Tricuspid valve
- Bicuspid valve
- Mitral valve
When cleaning a wound at least 250mL of Normal Saline should be used.
- True
- False
Upon arriving at the scene of a motor vehicle crash, you find the driver of the car still seated i her two door vehicle. The passenger side of the vehicle has sustained severe damage and is inaccessible. The driver is conscious and alert and complains only of lower back pain. The backseat passenger, a young child who was unrestrained, is bleeding from the head and appears to be unconscious. You should
- Ask the driver to step out the vehicle so can access the backseat passenger
- Rapidly extricate the driver so you can gain quick access to the child in the backseat
- Carefully assess the driver for occult injuries before removing her from the vehicle
- Apply a vest-type extrication device to the driver and quickly remove her from the car
A 30 year old man presents with jaw and neck stiffness and fever. During your assessment, he tells you that he cut his hand on a piece of metal about a week ago. ou should be most suspicious that this patient has
- Tetanus
- Meningitis
- A viral infection
- A staph infection
Full thickness circumfrential burns to the chest
- Require the paramedic to incise the burn to decompress it
- May cause significant restriction of respiratory excursion
- Are generally not significant unless the skin is unyielding
- Necessitate immediate intubation and ventilatory support
Approximately 80% of ventricular filling occurs
- During systole
- During diastole
- When the semilunar valves are open
- When the atrioventricular valves close
The ______ consists of eight bones that encase and protect the brain
- Skull
- Cerebrum
- Cranial vault
- Cribiform plate
Why do you want to give Morphine to an ACS patient?
- Dilates coronary arteries and vascular smooth muscle in veins, arteries, and arterioles.
- May limit ischemic myocardial injury, reducing the amount of ST segment elevation.
- Inhibits Thromoxane A2 platelet aggregation to reduce coronary reocclusion and recurrent events after fibrinolytic therapy.
- Dilates arteries and veins, which redistributes blood volume and reduces ventricluar preload and afterload.
Which of the following chemicals or drugs can cause an increase in heart rate
- Norepinephrine
- Cholinesterase
- Atenolol and neostigmine
- Atropine and epinephrine
The outer zone of an entrance or exit wound caused by a contract electrical burn is
- The red zone of coagulation necrosis
- Simply caused by local inflammation
- A charred area of full thickness burn
- Characterized by cold, gray, dry tissue
no image
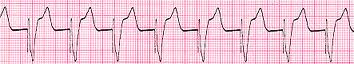
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Asystole
- 3rd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Inferior MI
- 1st Degree Heart Block
- Failure To Capture
- 2nd Degree Heart Block
- Acute Anterior MI
- Torsades
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Paced Rhythm
- Atrial Flutter
- Atrial Tachycardia
- Sinus Bradycardia
- Atrial Fibrillation
Decerebrate posturing is characterized by
- Flexion of the arms and extension of the legs
- Inward flexion of the wrists and flexed knees
- Extension of the arms and extension of the legs
- Pulling in of the arms toward the core of the body
A patient who is hyperventilating may have which acid-base condition?
- Respiratory acidosis
- Metabolic acidosis
- Metabolic alkalosis
- Respiratory alkalosis
The self splinting effect observed in patients with chest wall trauma
- Allows the body to compensate for the injury
- May cause atelectasis, hypoxemia, or pneumonia
- Is often accompanied by subcutaneous emphysema
- Is characterized by a markedly increased tidal volume
A 41 year old man was assaulted during a robbery attempt. Your initial assessment reveals that the patient is semiconscious. He has massive soft tissue trauma to the face, inadequate breathing, and oropharyngeal bleeding. You should
- Apply direct pressure to his facial wounds and promptly intubate him
- Suction the blood from his mouth and assist ventilations with a BVM
- Insert a nasal airway, apply oxygen via nonrebreathing mask, and transport
- Suction his oropharynx for 30 seconds and then perform endotracheal intubation
Pulse pressure (pp) is considered the _____.
- Difference between the systolic and diastolic pressure
- The sum of the systolic and diastolic pressure
- The inverse of the blood pressure
- Half of the systolic pressure
What are the 7 D's of Stroke Care?
- Dispatch, Door, Date, Decleration, Drug, Decision, Diazepam
- Dispatch, Door, Date, Detection, Drug, Diazepam, Delivery
- Detection, Dispatch, Delivery, Data, Decision, Drug, Diazepam
- Detection, Dispatch, Delivery, Door, Data, Decision, Drug
A young woman is complaining of sudden onset of right-sided abdominal pain. She admits to being sexually active and states she missed her last period. What do you suspect is the patient's likely diagnosis?
- PID
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Endometriosis
- Mittleschmertz
All of the following are considered new non-traditional roles for the paramedic except
- Primary care
- Sports medicine
- Family practitioner
- Industrial medicine
You are treating a 20 year old man with a large laceration involving the brachial artery. The patient is confused, pale, and has a weak carotid pulse. Your initial attempts to control the bleeding have failed you should
- Apply and inflate the PASG, start two large bore IV lines with an isotonic crystalloid, and transport.
- Give oxygen via non rebreathing mask, start a large bore IV of lactated ringers or normal saline, and transport
- Administer high flow oxygen, transport immediately, and attempt other bleeding control methods en route
- Perform endotracheal intubation, administer crystalloid fluids until his carotid pulse strengthens, and transport at once
The degree of absorption of a corrosive chemical determines
- The type of liquid used to irrigate the burn
- Whether the burn should be flushed
- Whether toxicity is local or systemic
- The antidote required to reverse the effects
On a 12 lead what does Leads I, II, and aVF show you?
- Lateral
- Inferior
- Septal
- Anterior
The rescuer's initial ventilation of a requiring CPR should be:
- Four quick breaths
- One quick breath
- Two full breaths
- Five full breaths
A woman finds her 50 year old husband unresponsive on the couch. When you arrive and begin your assessment, the wife tells you that her husband experienced an episode of chest discomfort 2 days prior, but refused to seek medical attention. The patient is unconsious and unresponsive, is breathing with a marked reduction in tidal volume, and has a rapid thready radial pulses. Your partner reports that the patients systolic BP is 70 mm Hg. The most appropriate treatment for this patient involves-
- Administering high flow oxygen via nonrebreathing mask, monitoring his cardiac rhythm, starting a large bore IV and giving a 20 ml/kg crystalloid bolus, initiating transport and infusing dopamine at 10-20 mcg/kg/min while en route to the closest facility
- Applying a CPAP device, monitoring his cardiac rhythm for dysrhythmias, establishing IV or IO access at the scene, administering a 500 mL crystalloid bolus, initiating transport, and administering atropine en route to prevent bradycardia
- Hyperventilating him with a BVM device for 2-3 minutes, intubating his trachea, establishing vascular access, administering prophylactic amiodarone to prevent ventricular dysrhythmias, and transporting him while infusing crystalloid fluid boluses en route to the hospital
- Assisting his ventilations, applying a cardiac monitor, intubating if necessary, auscultating his lungs, transporting at once, establishing vascular access en route, administering a 200 mL crystalloid bolus if his lungs are clear and considering a dopamine infusion
Because of its weight bearing capacity, the _______ spine is especially susceptible to injury
- Cervical
- Thoracic
- Lumbar
- Coccygeal
What is pH?
- The phosphorus level
- The oxygen saturation
- The hydrogen ion concentration
- The hemoglogin level
Which of the following statements regarding thte nasal septum is most correct
- It may be slightly deviated to one side or the other
- The nasal septum is comprised mainly of cartilage
- Inflammation of the nasal septum is common during infection
- The nasal septum separates the oropharynx and nasopharynx
To keep up this site, we need your assistance. A little gift will help us alot.
Donate- The more you give the more you receive.
Related SubjectSouthern California Wildfire Risks and Winds
Severe Weather and Travel Delays
Northern Gaza Hospitals
Azerbaijan Airlines Crash in Kazakhstan
Winter Survival Skills
Ventura County Wildfire
Public Safety Dispatcher
Emergency and Disaster Management
Emergency Medical Services
Phlebotomy
Medical Office Administration
Nursing: Registered Nurse
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Diagnostic Cardiac Sonography
Cannabis Science and Therapeutics
Microbiology and Parasitology
Introduction to Psychology
Certified Nursing Assistant
Healthcare Studies
Health and Human Services in Focus
Physical Therapist Assistant
Public Health
Medical Assistant
Health Sciences
Health Care Office Manager
Dietetic Internship
Nursing Interventions: Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Secondary Education
Psychology
Middle School Education
Early Childhood Education
Education
Community Health Worker
Technology for teaching and learning in Elementary Grades
Teacher and the School Curriculum
Teaching Math in the Intermediate Grades
Risk Management Applied to Safety Security and Sanitation
Risk Management
Recruitment and Selection
Health Assessment
Show All Subject
Affiliate Links
Shopee Cashback Voucher
Temu $0 Shipping Fee
Amazon 75% Off Discounts